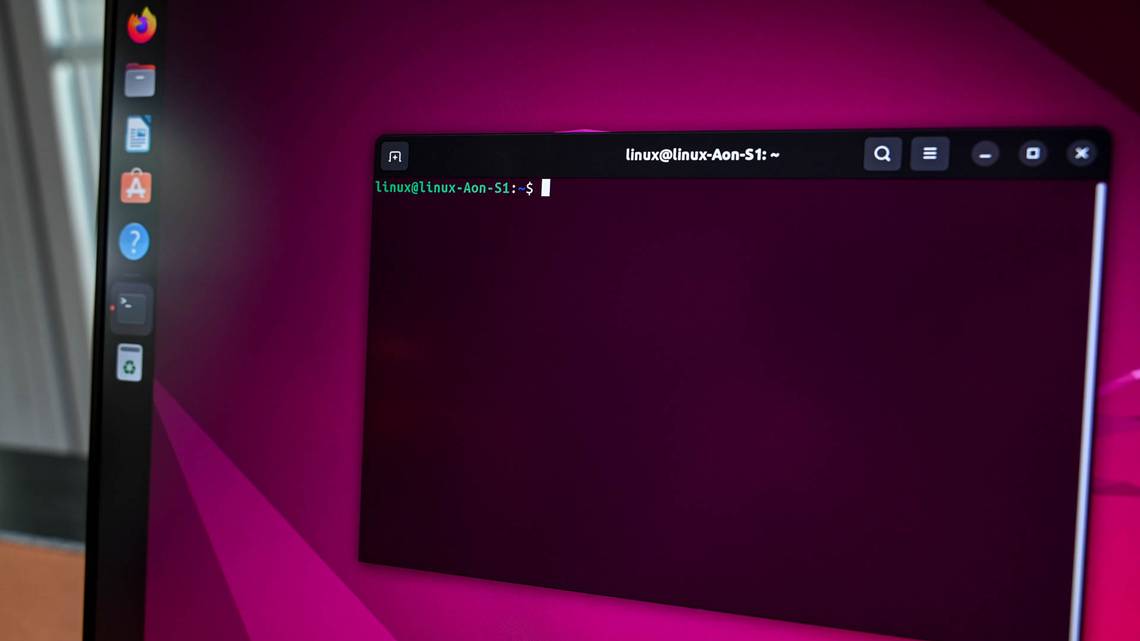
To install the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) on Windows 11, run Terminal as administrator, then enter “wsl –install” into the window. Run “wsl –install -d Distro”, replacing “Distro” with the name of a Linux distro, to install a specific distribution instead of Ubuntu. You can install additional Linux distros from the Terminal or the Microsoft Store.
The Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) lets you run Linux software on your Windows 11 PC. When you enable WSL, Windows will install a custom-built Linux kernel. You can then install Ubuntu or another Linux distribution of your choice.
[mai mult...]