How to creating Bar Charts using the REPT Function in Excel
Another way to create in-cell bar charts is to use the REPT function, which repeats a specified character a given number of times.
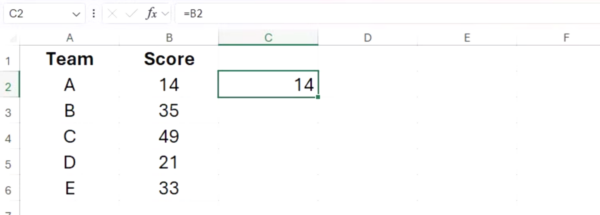
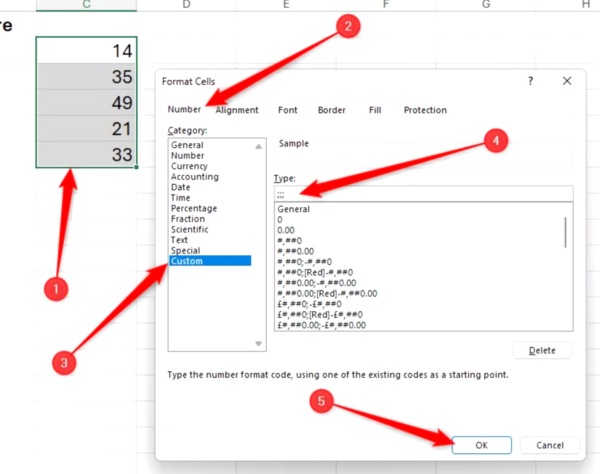
In the cell next to the first value you want to visualize, type:
=REPT("|",x)
and press Ctrl+Enter.
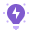
In this formula, “|” is the vertical glyph character (enclosed in double quotes) often accessed by pressing Shift or Fn at the same time as the relevant key, and x is a reference to a cell containing a numerical value. Here, the formula references cell B2 and so returns 14 vertical glyphs.
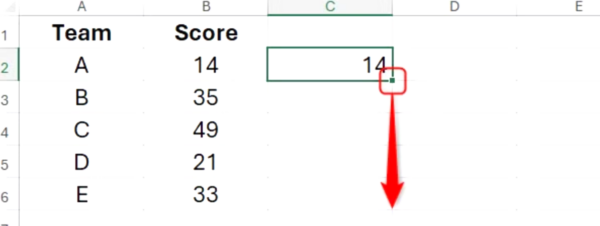
Double-click the fill handle of that cell to repeat the formula down the column.
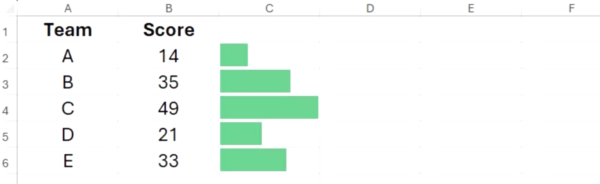
At the moment, the data is visualized as a tally graph, as the default fonts in Excel place small spaces between each character. To fix this, select the relevant cells, and in the Home tab on the ribbon, select a typeface that doesn’t separate characters with a space, like “Stencil” or “Playbill.”
Where data bars adjust to the column width, bar charts created using the REPT function expand or contract dynamically, regardless of the width of the cells they occupy.
[mai mult...]