Situatie
The exponential growth of the event technology sector has placed platforms at the nexus of high-volume personal data collection. Today’s event ecosystem relies on sophisticated tools, from AI-powered personalization to seamless biometric check-ins, which inherently elevate the organization’s responsibility and liability profile. For event organizers and technology providers operating in the United States, data security is no longer an ancillary feature or a compliance checkbox; it is a fundamental strategic imperative and a defining factor in market valuation and brand resilience.
This analysis identifies the non-negotiable standards, from regulatory adherence and operational controls to forward-looking architectural strategies, required to safeguard attendee information in an environment defined by escalating cyber threats and punitive regulatory frameworks.
Solutie
The new high-value target: redefining attendee data
Event technology platforms are no longer handling simple contact lists. They are centralized repositories of highly sensitive Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and increasingly, biometrics. PII encompasses foundational identifiers such as phone numbers, age, gender, and date of birth. Depending on the scope of the event (e.g., financial or large-scale industry events), this can extend to social security numbers or credit card details.
Modern engagement tools have introduced biometric data into the event lifecycle. Technology such as facial recognition, utilized for streamlining check-ins and improving security, relies on biological details like fingerprints or iris structures. The incorporation of these identifiers fundamentally alters the regulatory liability profile, automatically triggering the most stringent privacy mandates.
The inherent increase in risk requires a proactive approach to the data lifecycle. Beyond merely securing the data during collection and use, platforms must adopt data deletion as a core principle. To build long-term trust with increasingly privacy-conscious audiences and comply with global “Right to Erasure” provisions, it is non-negotiable that attendees have the ability to request data deletion post-event. Failure to implement robust data minimization and compliant deletion frameworks subjects the organization to indefinite regulatory risk.
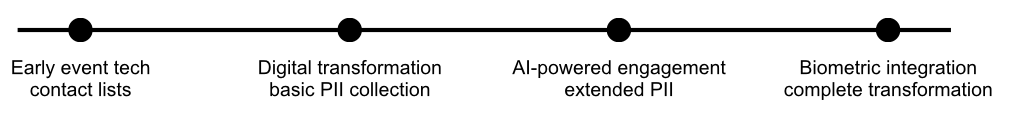
The evolution of event technology data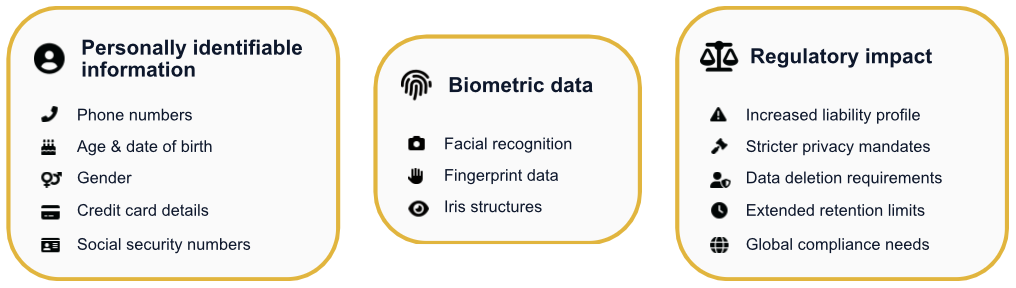
Quantifying the financial and reputational risk
Security investment must be understood as a mandatory cost-avoidance strategy. Statistical data confirms that the financial repercussions of negligence in the United States are uniquely severe, justifying preemptive action.
The average cost of a data breach for U.S. companies has reached an unprecedented peak, hitting $10.22 million in 2025. This figure represents a significant 9% increase over previous years and signals a unique and heightened risk environment within the country. This stark financial reality stands in contrast to the global average cost of $4.44 million, which saw a decline in the same period.
This extreme disparity demonstrates that the high expense is primarily driven by external forces: specifically, higher regulatory fines and the high internal costs associated with detection and escalation. Furthermore, recovery efforts following a breach typically extend beyond 100 days, with a significant proportion of organizations taking up to 150 days to recover fully. The analysis indicates that slow detection directly correlates with the final financial consequence, making rapid incident response a primary financial non-negotiable.
Targeted vulnerability: the hospitality and event sector exposure
The event sector, particularly its adjacent hospitality firms, carries an elevated risk profile due to the high volume of customer information processed. The average cost of a hospitality data breach is estimated at $4.03 million in 2025.
This sharp financial impact is compounded by persistent security gaps at the periphery of the network. Projections for 2025 indicate that 60% of cyberattacks targeting the hospitality and event-adjacent sectors will originate from vulnerabilities found in connected devices, such as point-of-sale (POS) terminals and various IoT equipment. This means that a robust defense strategy cannot solely focus on core servers; the security scope must be non-negotiably extended to every device used on the event floor, as these peripheral systems often represent the weakest link.
The catastrophic long-term erosion of enterprise value
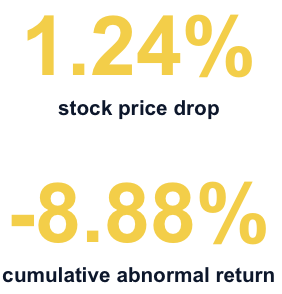 While immediate costs dominate news cycles, the true price of a breach is the sustained damage to brand equity. Announcement of a data breach causes an immediate stock price drop of approximately 1.24% for affected firms.However, the long-term impact on enterprise value is far more damaging.
While immediate costs dominate news cycles, the true price of a breach is the sustained damage to brand equity. Announcement of a data breach causes an immediate stock price drop of approximately 1.24% for affected firms.However, the long-term impact on enterprise value is far more damaging.
Research confirms that these events have significant negative abnormal returns, culminating in an average cumulative abnormal return of –8.88% for hospitality firms 12 months post-announcement. This long-term erosion underscores that robust security is necessary not just for short-term compliance, but for preserving core market value and maintaining investor confidence.
Robust security is necessary for preserving core market value. Security investment must be understood as a mandatory cost-avoidance strategy. In the event technology landscape, data security is a fundamental strategic imperative for market valuation and brand resilience.



Leave A Comment?