Situatie
Let’s compare the different types of RAM memory channels: single-channel, dual-channel, triple-channel, and quad-channel. Here are the key differences and considerations for each type:
Solutie
1. Single-Channel RAM
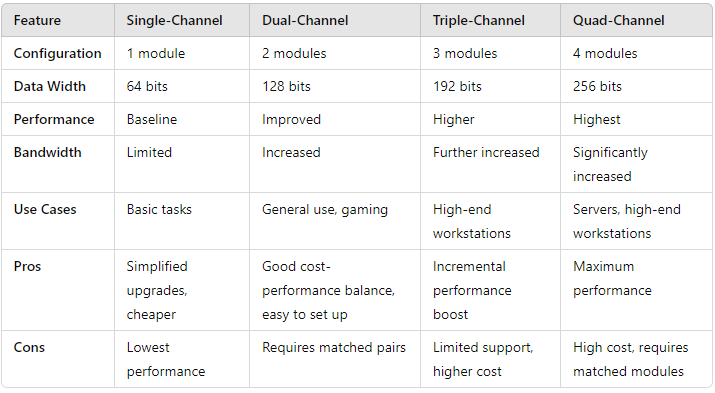
- Configuration: Utilizes one RAM module.
- Performance: Provides the baseline performance for a given RAM stick.
- Bandwidth: Limited to the bandwidth of a single RAM module, meaning lower data transfer rates.
- Use Cases: Suitable for basic tasks such as web browsing, office applications, and low-end gaming.
- Pros: Simplifies upgrades (add one stick at a time) and is often cheaper.
- Cons: Offers the lowest performance and is not ideal for demanding applications or multitasking.
2. Dual-Channel RAM
- Configuration: Uses two RAM modules in matched pairs.
- Performance: Effectively doubles the data width to 128 bits, offering a significant performance boost over single-channel.
- Bandwidth: Increased, providing better data transfer rates and overall system performance.
- Use Cases: Ideal for most users, including gamers, content creators, and general multitasking.
- Pros: Balances cost and performance, easy to set up with most modern motherboards supporting dual-channel.
- Cons: Requires matched pairs for optimal performance, slight increase in complexity when upgrading.
3. Triple-Channel RAM
- Configuration: Uses three RAM modules in matched sets.
- Performance: Increases the data width to 192 bits, providing higher performance than dual-channel.
- Bandwidth: Further improved, suitable for more demanding applications.
- Use Cases: Less common, mainly used in specific high-end or older workstation systems.
- Pros: Provides an incremental performance boost over dual-channel.
- Cons: Limited support in modern motherboards, more complex configuration, and higher cost per module.
4. Quad-Channel RAM
- Configuration: Utilizes four RAM modules in matched sets.
- Performance: Increases the data width to 256 bits, offering the highest performance among standard consumer configurations.
- Bandwidth: Significantly increased, optimal for data-intensive tasks.
- Use Cases: Ideal for high-end workstations, servers, and users with intensive workloads such as video editing, 3D rendering, and heavy multitasking.
- Pros: Provides maximum performance, optimal for memory bandwidth-intensive applications.
- Cons: Higher cost, requires four matched modules, supported mainly on high-end motherboards.
Summary Table
Key Takeaways
- Single-channel is suitable for basic tasks and is cost-effective.
- Dual-channel is the most balanced option for most users, offering a good mix of performance and affordability.
- Triple-channel and quad-channel provide higher performance but are more complex and expensive, suitable for specific high-end applications and professional use cases.
When choosing RAM, consider the specific needs of your applications and workloads, as well as the compatibility and support of your motherboard.

Leave A Comment?