Situatie
Solutie
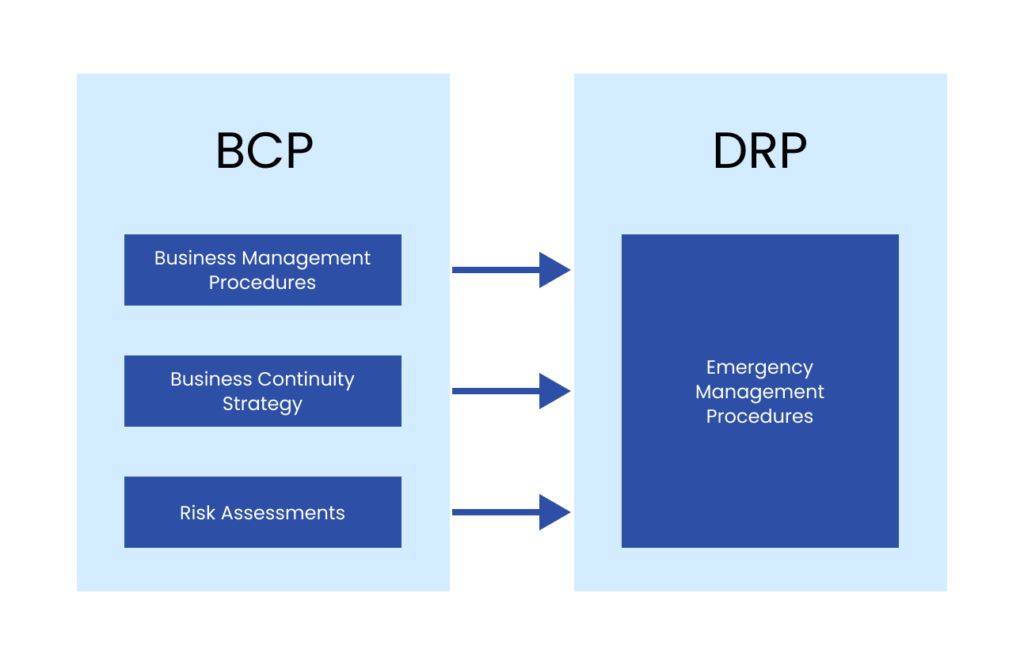
A business continuity plan (BCP) is a document that outlines how a business will continue operating during an unplanned disruption in service. It’s more comprehensive than a disaster recovery plan and contains contingencies for business processes, assets, human resources and business partners – every aspect of the business that might be affected.
Plans typically contain a checklist that includes supplies and equipment, data backups and backup site locations. Plans can also identify plan administrators and include contact information for emergency responders, key personnel and backup site providers. Plans may provide detailed strategies on how business operations can be maintained for both short-term and long-term outages.
A key component of a business continuity plan (BCP) is a disaster recovery plan that contains strategies for handling IT disruptions to networks, servers, personal computers and mobile devices. The plan should cover how to reestablish office productivity and enterprise software so that key business needs can be met. Manual workarounds should be outlined in the plan, so operations can continue until computer systems can be restored.
There are three primary aspects to a business continuity plan for key applications and processes:
- High availability: Provide for the capability and processes so that a business has access to applications regardless of local failures. These failures might be in the business processes, in the physical facilities or in the IT hardware or software.
- Continuous operations: Safeguard the ability to keep things running during a disruption, as well as during planned outages such as scheduled backups or planned maintenance.
- Disaster recovery: Establish a way to recover a data center at a different site if a disaster destroys the primary site or otherwise renders it inoperable.
What is Data Loss Prevention?
Data loss prevention, also known as DLP or data loss protection, is a software strategy used by most businesses today. DLP encompasses a set of tools and best practices designed to protect an organization’s data from loss, corruption, or unauthorized access by employees or anyone outside the network.
One of the most significant components of DLP is in classifying data and applying policies, many of which are driven by compliance regulations like the GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS. If the DLP software detects policy violations, it initializes a remediation process, including enforcing or imposing encryption, alerts, and data isolation to prevent sharing, downloading, or transferring sensitive data out of the network.
What is a Disaster Recovery Plan?
A disaster recovery plan (DRP), disaster recovery implementation plan, or an IT disaster recovery plan is a document that helps an organisation handle unexpected incidents, such as cyber-attacks, natural disasters, power outages. They have the potential to shut down a company’s IT systems and hinder its overall operations.
A DRP aims to get your business up and running as quickly as possible during a disaster or data breach. With an effective disaster recovery plan, there is less chance of you losing out on profits for too long. Also, it should have backups set in place to prevent sensitive data (social security numbers or credit card information) from getting compromised.
Why is a Disaster Recovery Plan important?
Data loss, downtime, and tech outages are some of the new horror stories that even the top companies are going through nowadays. Whenever a disaster strikes in a company, the engineering teams rush to repair the damage, and on the other hand, PR teams work overtime to restore customer confidence.
Don’t you think it is a time-consuming and expensive effort?
Of course, it is!
Top 4 Benefits of the Disaster Recovery plan:
- Minimising the recovery time & possible delays
- Train employees about safety procedures in case of an emergency
- Safeguards financial data and improves security
- Describe operational alternatives well in advance
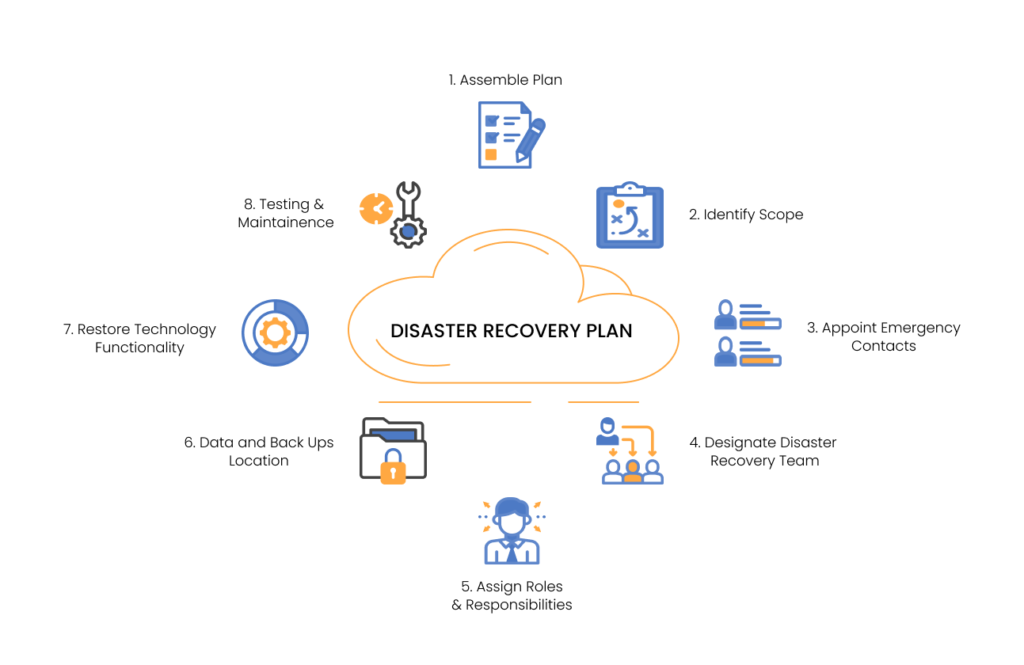
Disaster Recovery Plan and Business Continuity Plan – Are they Correlated?
Business continuity refers to how a company keeps running in the event of a natural or man-made disruption. On the other hand, a DRP is concerned with restoring normal business-critical operations after a disaster. It can be said that a DRP is more focused, and it is a specific part of a wider business continuity plan(BCP).
Pro tip-It is most effective to develop information technology (IT) disaster recovery plan in conjunction with the business continuity plan (BCP).
Whether you maintain your disaster recovery plan internally or outsource it to a managed service provider, or use any disaster recovery plan template, the document must contain complete, accurate, and up-to-date information on your company’s IT activities. The top management, IT management, human resources and finance specialists, and the security department are collectively responsible for outlining, implementing, testing, and maintaining the disaster recovery plan.
Data loss prevention and protection solutions are also used to monitor access and activity within the system, such as through email or instant messaging. By doing so, organizations mitigate the risk of accidental or intentional exposure of sensitive data beyond authorized channels. If a leak or breach is detected, the DLP system applies pre-set protocols to encrypt, isolate, and protect company data, even after it’s left the system.

Leave A Comment?