Situatie
If you’re unsure whether you permanently deleted a file, look around for it first. Try performing a search in File Explorer. Hopefully, you just misplaced the file and you can find it again.
You might also want to check your external storage drives, such as flash drives, HDDs, and SDDs, in case you moved the file there and don’t remember.
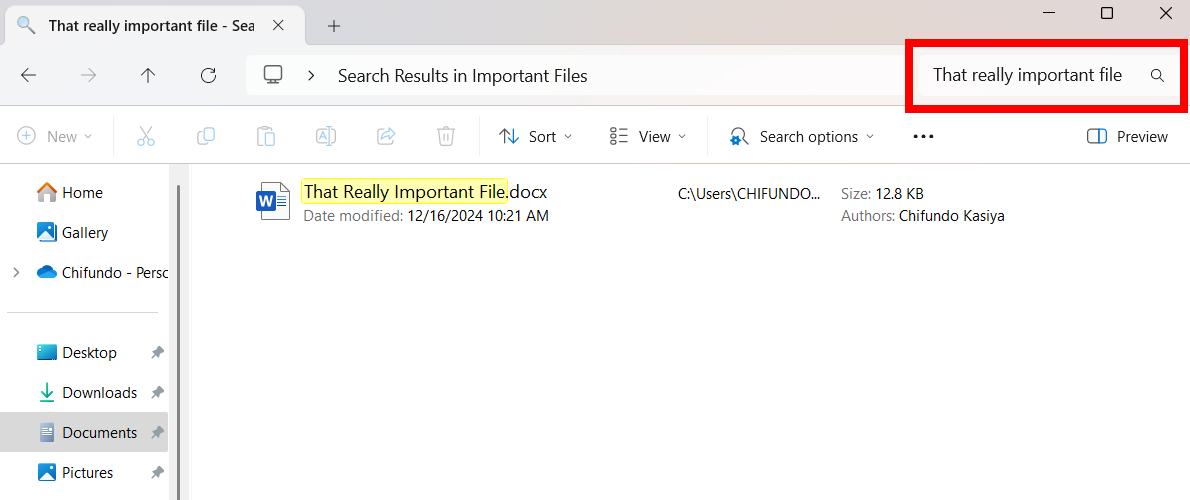
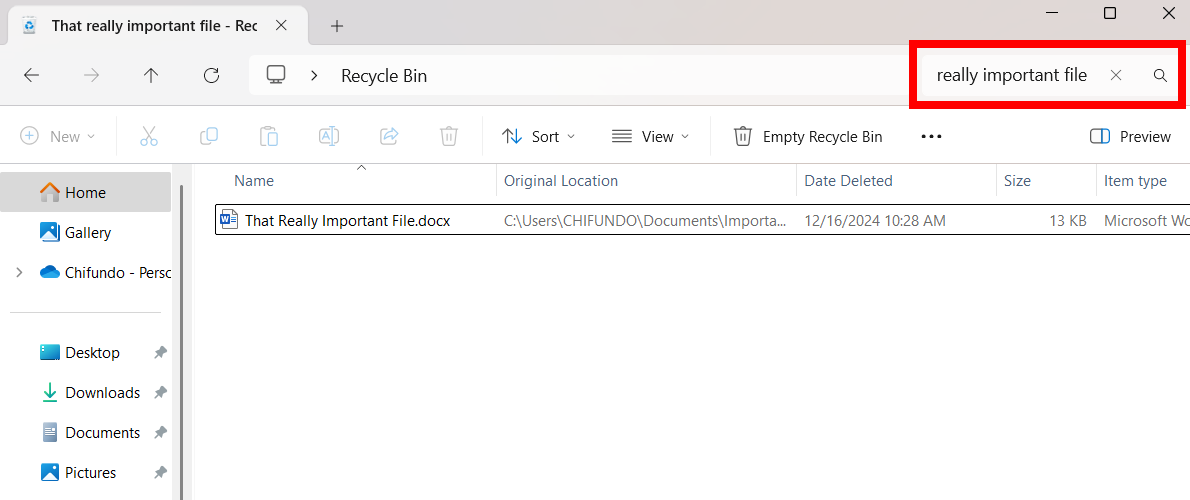
You can also peek inside the Recycle Bin. If you have a lot of files in there, you can use the search box in the top-right corner of the window to search for the file.
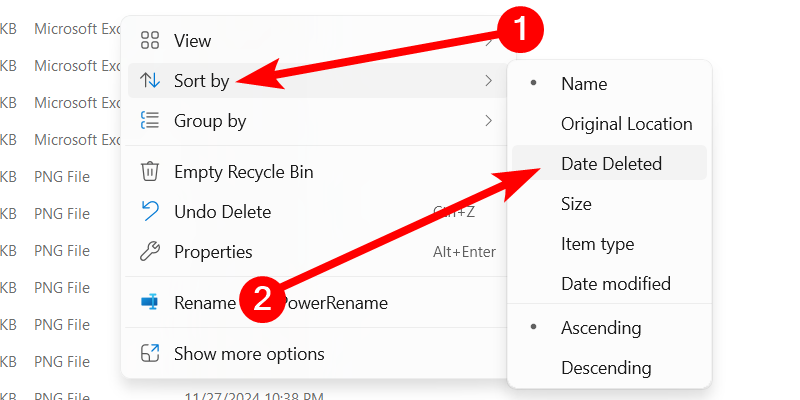
You can also right-click in the Recycle Bin window and select Sort By > Date Deleted to more easily view recently deleted files.
If your file was stored in a cloud storage service like OneDrive, Google Drive, or Dropbox, log into your account on the service’s website and check your deleted files there—you may find the file is still recoverable. This is the cloud storage version of the Recycle Bin.
On OneDrive, for instance, click the “Recycle Bin”—the trash can icon—in the left sidebar to see your recently deleted files. Keep in mind that these will only remain in OneDrive for 30 days if it is your personal OneDrive.
Windows File History tool is useful for easily recovering deleted files and older versions of files from an external drive. It backs up files from specific locations, such as Libraries, Desktop, Contacts, and Favorites. If you enabled File History (it’s disabled by default), all you have to do is use it to recover the file.
File History saves the state of the included folders at a specific time. That means you will be reverting the entire folder to a previous version, and you may lose your recent files. Use this option if the deleted file is extremely important.
Microsoft has a tool for recovering deleted and corrupted files on Windows. It’s called Windows File Recover, and it’s an easy-to-use command-line tool that ensures your files aren’t permanently lost.
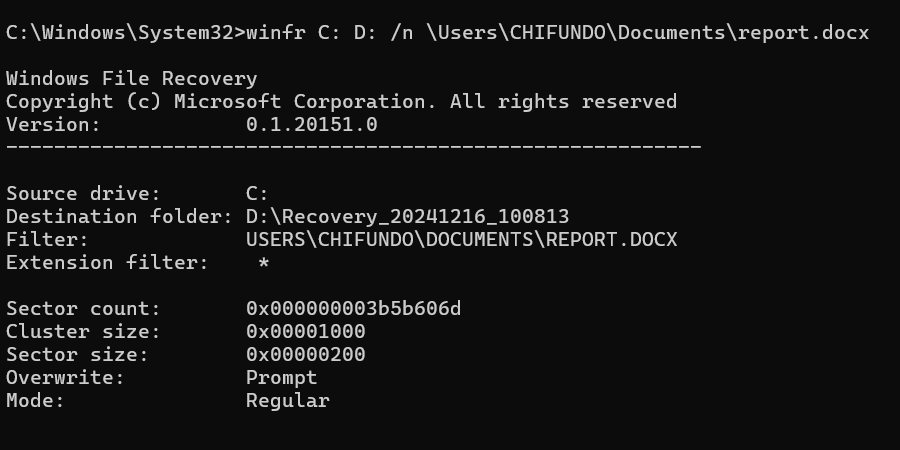
Once you install Windows File Recovery, launch it by opening the Start Menu, typing Windows File Recover in the search box, and selecting it when it appears in the search results. You need to know which commands to use to find the deleted file, but since this is not an in-depth tutorial on how to use this tool, I will just use an example of finding a find named report.docx.
The command for this would look like this:
winfr C: D: /n \Users\CHIFUNDO\Documents\report.docx
In the above command, C: is the drive to check for the deleted file (source drive), and D: is the drive to store it once found (destination drive). The /n is called a switch, which is a modifier that tells the command to target specific files or folders. The file path afterward tells Windows File Recovery where to find the file on the C: drive.

Leave A Comment?