Situatie
Solutie
Before i show you some examples of each function in action, here are their syntaxes.
The TRANSLATE function has three arguments:
=TRANSLATE(a,b,c)
where
- a (required) is either the text to translate (embedded in double quotes), or a reference to the cell containing the text to translate.
- b (optional) is the source language code in double quotes (see the Language Codes section below). If you omit this argument, Excel will try to detect the language automatically. Although this is an optional argument, it’s best to include it (if you know the language and its code) to ensure an accurate translation.
- c (optional) is the target language in double quotes. If you skip this argument, Excel will use your system language as the target language. However, again, try to add a target language code for better translation outcomes.
This function is much more straightforward, requiring only one argument:
=DETECTLANGUAGE(x)
where
- x is either the text to detect, embedded within double quotes, or a reference to the cell containing the text to detect.
Here are some of the language codes from Microsoft’s longer list of codes. Remember that all language codes in your formula must be in double quotes.
| Code | Language |
|---|---|
| “en” | English |
| “es” | Spanish |
| “fr” | French |
| “de” | German |
| “zh-chs” | Mandarin (simplified) |
| “ru” | Russian |
| “ar” | Arabic |
Example 1: Translating Text in Cells
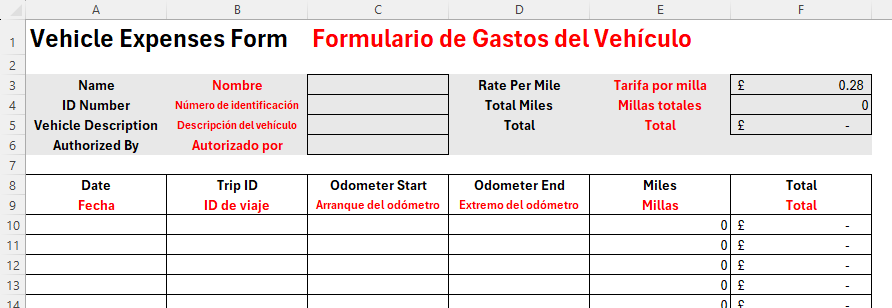
Let’s say you have a vehicle expenses form, and you want to translate the form’s title, totals section, and table headers from English into Spanish.
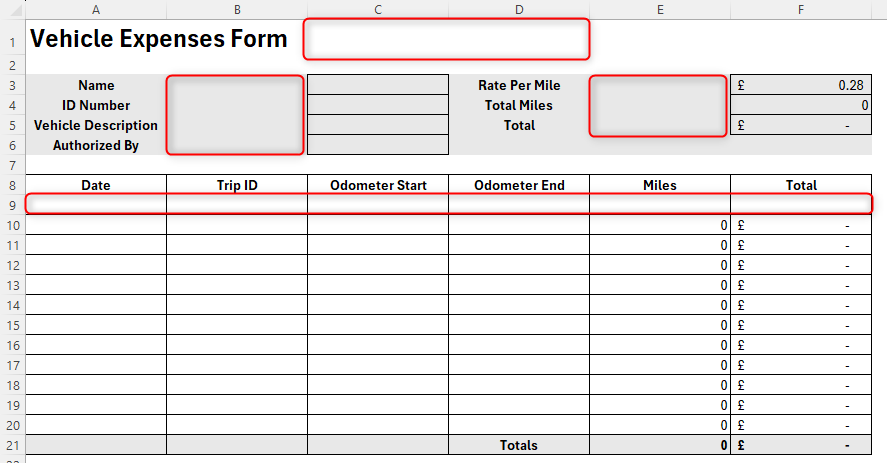
Starting in cell C2, type:
=TRANSLATE(A1,"en","es")
and press Enter.
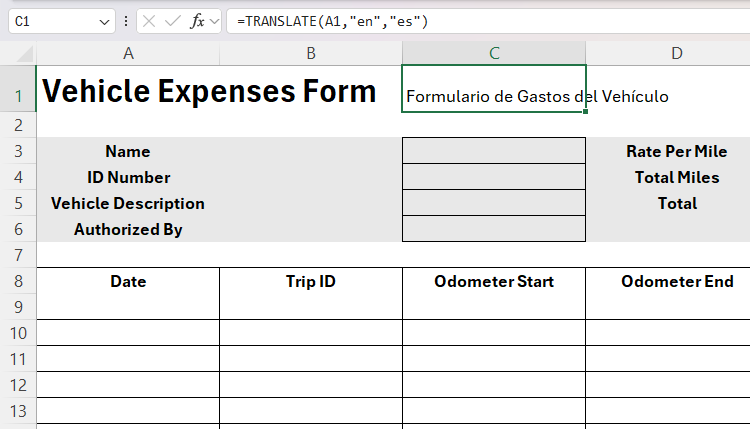
Now, use the format painter tool to apply the formatting of the English title to the Spanish title. You can also apply a red font to distinguish between the two languages.
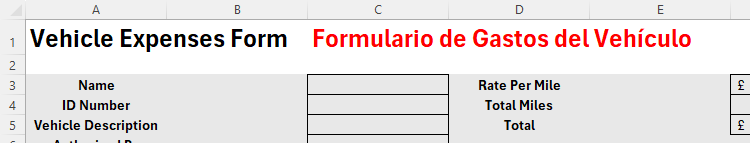
You’re now ready to translate the next section of the form. First, select cell C1, and select and copy (Ctrl+C) the formula in the formula bar.
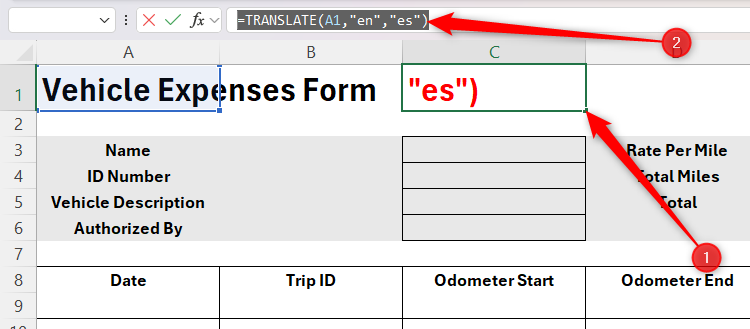
Now, select cell B3, paste (Ctrl+V) the copied formula into the formula bar, and change the first argument to reference cell A3, before pressing Enter.
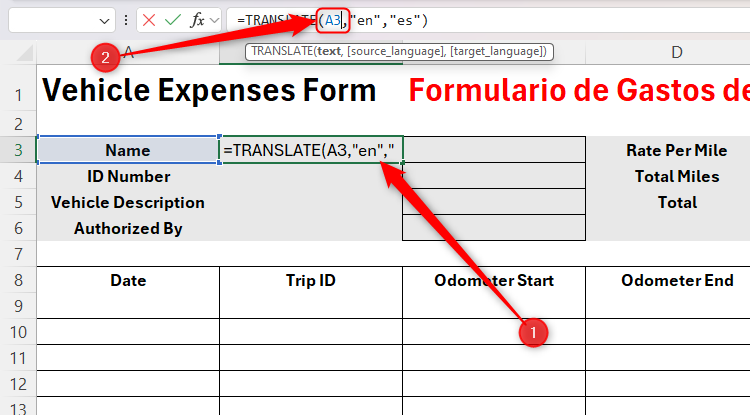
Now, use the fill handle to apply the same relative formula to cells B4 to B6
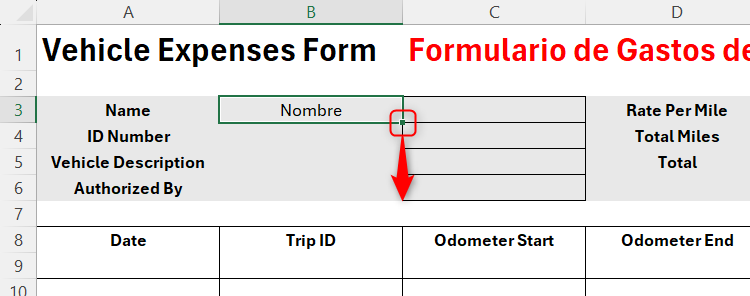
To finish this section, copy and paste the formula into cell E3, and use the fill handle again.
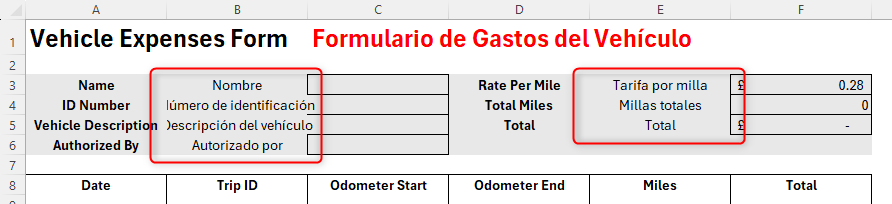

Because some of the Spanish translations contain more characters than their English counterparts, adjust the font sizes (or, if you prefer, the column widths) so that they fit nicely into their respective cells. Remember to also change the font colors to red for consistency.
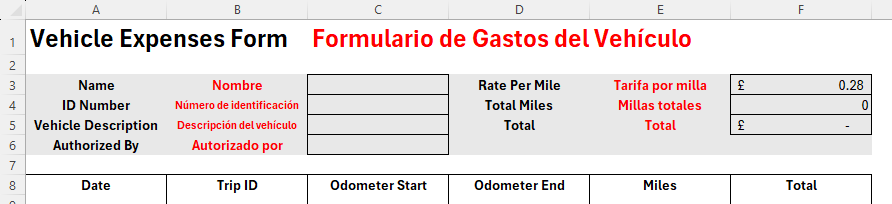
Finally, follow the same process to translate your table headers.

Leave A Comment?