Situatie
We will be using the Linux command line tool, the Terminal, in order to compile a simple C program. To open the Terminal, you can use the Ubuntu Dash or the Ctrl+Alt+T shortcut.
Backup
Solutie
Pasi de urmat
Step 1: Install the build-essential packages
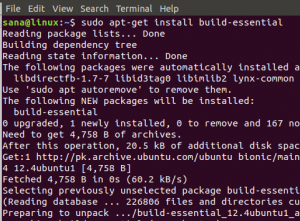
In order to compile and execute a C program, you need to have the essential packages installed on your system. Enter the following command as root in your Linux Terminal:
$ sudo apt-get install build-essential
You will be asked to enter the password for root; the installation process will begin after that.
Please make sure that you are connected to the internet.
Step 2: Write a simple C program
After installing the essential packages, let us write a simple C program.
Open Ubuntu’s graphical Text Editor and write or copy the following sample program into it:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("\nA sample C program\n\n");
return 0;
}
Then save the file with .c extension. In this example, I am naming my C program as sampleProgram.c
 Alternatively, you can write the C program through the Terminal in gedit as follows:
$ gedit sampleProgram.c
This will create a .c file where you can write and save a program.
Alternatively, you can write the C program through the Terminal in gedit as follows:
$ gedit sampleProgram.c
This will create a .c file where you can write and save a program.
Step 3: Compile the C program with gcc
In your Terminal, enter the following command in order to make an executable version of the program you have written:
Syntax:
$ gcc [programName].c -o programName
Example:
$ gcc sampleProgram.c -o sampleProgramMake sure your program is located in your Home folder. Otherwise, you will need to specify appropriate paths in this command.
Step 4: Run the program
The final step is to run the compiled C program. Use the following syntax to do so:
$ ./programName Example:
$ ./sampleProgramYou can see how the program is executed in the above example, displaying the text we wrote to print through it.

Leave A Comment?