Situatie
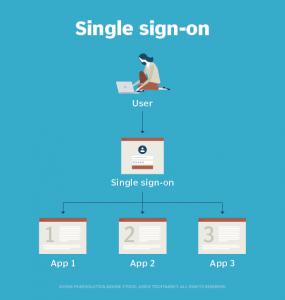
Single sign-on (SSO) is a session and user authenticatication service that permits a user to use one set of login credentials — for example, a name and password — to access multiple applications. SSO can be used by enterprises, smaller organizations and individuals to ease the management of various usernames and passwords.
Solutie
Pasi de urmat
In a basic web SSO service, an agent module on the application server retrieves the specific authentication credentials for an individual user from a dedicated SSO policy server, while authenticating the user against a user repository, such as a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory. The service authenticates the end user for all the applications the user has been given rights to and eliminates future password prompts for individual applications during the same session.
How single sign-on works
Single sign-on is a federated identity management (FIM) arrangement, and the use of such a system is sometimes called identity federation. OAutch, which stands for Open Authorization and is pronounced “oh-auth,” is the framework that enables an end user’s account information to be used by third-party services, such as Facebook, without exposing the user’s password.
OAuth acts as an intermediary on behalf of the end user by providing the service with an access token that authorizes specific account information to be shared. When a user attempts to access an application from the service provider, the service provider will send a request to the identity provider for authentication. The service provider will then verify the authentication and log the user in.

Leave A Comment?