Situatie
Compromised Domain Controllers are every Active Directory admin’s nightmare. However, Domain Controllers now have nightmares of their own … all through their Print Spooler services.
The vulnerability known as CVE-2021-1675 was believed to be fixed as part of the June 2021 cumulative updates. However, it has now been weaponized to elevate a standard domain user’s privileges to SYSTEM privileges on a Domain Controller. This trumps the entire privilege structure on Domain Controllers, undermining confidentiality, integrity and availability within Active Directory.
The code to compromise a fully patched Windows Server 2019-based Domain Controller was published publicly this Wednesday, making CVE-2021-1675 a zero-day vulnerability. As it is common for these types of vulnerabilities, it has a nickname: PrintNightmare.
Solutie
Pasi de urmat
A long history
Print Spooler vulnerabilities and Domain Controllers have a long history.
On March 11, 2021, an elevation of privilege (EoP) Print Spooler vulnerability was addressed during the March 2021 cumulative updates. CVE-2021-1640 featured a relatively low complexity and an attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could overwrite arbitrary file content in the security context of the local system.
On January 12, 2021, another low-complexity EoP Print Spooler vulnerability, CVE-2021-1695, was addressed as part of the January 2021 cumulative updates. In 2020, another six vulnerabilities were addressed throughout the May, August, September, and November cumulative updates. The addressed vulnerabilities were all EoP vulnerabilities, except for CVE-2020-17042. This was a remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability and caused headaches for many admins.
2020 was an exceptional year in the number of Print Spooler service vulnerabilities. 2019 featured two information disclosure vulnerabilities. 2018 featured one denial of service (DoS) vulnerability in the Print Spooler service. Looking all the way back to 2005, a dozen Print Spooler vulnerabilities, including buffer overflows, RCE and EoP vulnerabilities have been addressed in several Windows Server generations.
The role of the Print Spooler service on Domain Controllers
Microsoft published a whole list of services you can disable on Windows Server installations. However, there’s a reason why Microsoft hasn’t made the Printer Spooler service a part of the hardening guidelines on Windows Servers. On domain-joined devices and Windows Server installations, the Print Spooler service is responsible for printing documents and delivering them in certain formats (typically PCL or PS) and with certain preferences (typically targeting a specific tray) to printers through print queues.
On Domain Controllers, the Print Spooler service has another role. It is a far lesser-known role of the Print Spooler service. When an organization publishes printers in Active Directory, Domain Controllers check the availability of these print queues on print servers. When the print queues are no longer available, Domain Controllers delete these objects from Active Directory, automatically.
This feature is known as Pruning of published printers.
With default settings, the Print Spooler service on a Domain Controller contacts print servers every eight hours. If a print server doesn’t respond, the Domain Controller retries two times. When the print server doesn’t respond to these contact messages, or when the printer is no longer shared on the print server, the print queue is deleted from Active Directory. This way, printers in Active Directory are kept up to date.
Making the right choice
The obvious route to end today’s nightmares is to stop and disable the Print Spooler service on all Domain Controllers (and other Windows Server installations that do not act as print servers).
To make this choice as an Active Directory admin, you’ll need to know if and what print queues are published in Active Directory. Additionally, you’ll want to know if you’re using the default settings for printer pruning. Run the following line of code on a domain-joined device or Windows Server installation equipped with the Active Directory module for Windows PowerShell, to list the print queues that are published in Active Directory:
Get-AdObject –filter ”objectCategory -eq ‘printqueue'”
Then, use Resultant Set of Policy (rsop.ms) on one or more Domain Controllers to check the Group Policy settings for Printers underneath the Administrative Templates for the Computer Configuration. Specifically, you want to look at the configuration of the following three settings:
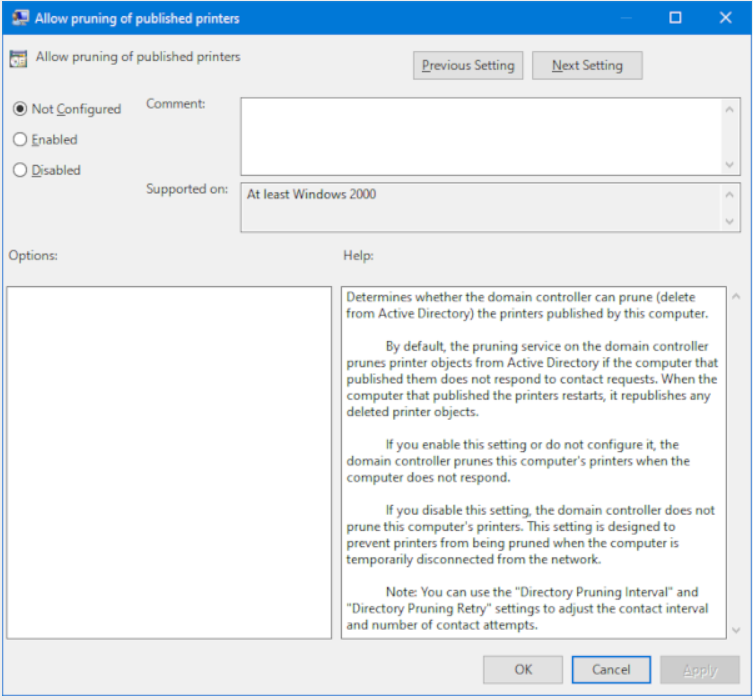
- The Allow pruning of published printers setting determines whether the Domain Controller can prune (that is, delete from Active Directory) the printers that are published by this computer. By default, the pruning service on the Domain Controller prunes printer objects from Active Directory if the computer that published them does not respond to contact requests. When the print server restarts, it republishes any deleted printer objects. If the setting is Not configured, Domain Controllers prune published printers from this print server.
- The Directory pruning interval setting determines the interval which with Domain Controllers check print servers. If the setting is Not configured, Domain Controllers check print servers every eight hours.
- The Directory pruning retry setting determines the number of retries for the pruning process. If the setting is Not configured, Domain Controllers retry two times.
As you can see, when all three settings are Not configured (the default settings), pruning of printers in Active Directory occurs every eight hours. Published printers are pruned within eight hours of the print queue being deleted on the print server, or within 24 hours when the print server hosting the print queue is no longer available.
When you disable the Print Spooler service on all Domain Controllers, printers will no longer be automatically pruned.

Leave A Comment?