Situatie
In Linux, file permissions are rules that determine who can access, modify, or execute files and directories. They are foundational to Linux security, ensuring that only authorized users or processes can interact with your data.
Solutie
Pasi de urmat
What are Permission Groups in Linux
First, you must think of those nine characters as three sets of three characters (see the box at the bottom). Each of the three “rwx” characters refers to a different operation you can perform on the file.
Owners: These permissions apply exclusively to the individuals who own the files or directories.
Groups: Permissions can be assigned to a specific group of users, impacting only those within that particular group.
All Users: These permissions apply universally to all users on the system, presenting the highest security risk. Assigning permissions to all users should be done cautiously to prevent potential security vulnerabilities.
--- --- --- rwx rwx rwx user group other
Symbolic notation allows you to add, remove, or set permissions for specific users. Let’s understand this using different example below:
To Change File Permission in Linux
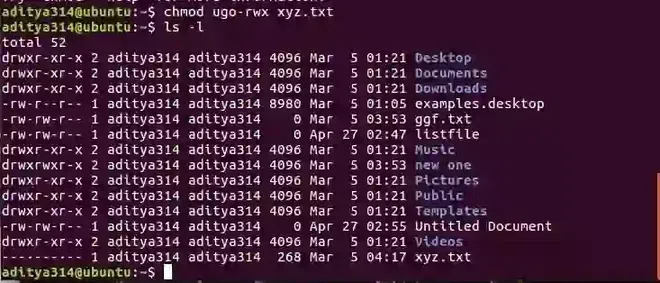
If you want to give “execute” permission to the world (“other”) for file “xyz.txt”, you will start by typing.
chmod o
Now you would type a ‘+’ to say that you are “adding” permission.
chmod o+
Then you would type an ‘x’ to say that you are adding “execute” permission.
chmod o+x
Finally, specify which file you are changing.
chmod o+x xyz.txt
You can also change multiple permissions at once. For example, if you want to take all permissions away from everyone, you would type.
chmod ugo-rwx xyz.txt

Leave A Comment?