Situatie
Most people assume that deleting files and emptying the Recycle Bin permanently removes them—but that’s not true. Those “deleted” files still sit on your drive and can be restored with recovery tools.
Solutie
How to set up sDelete for the first time
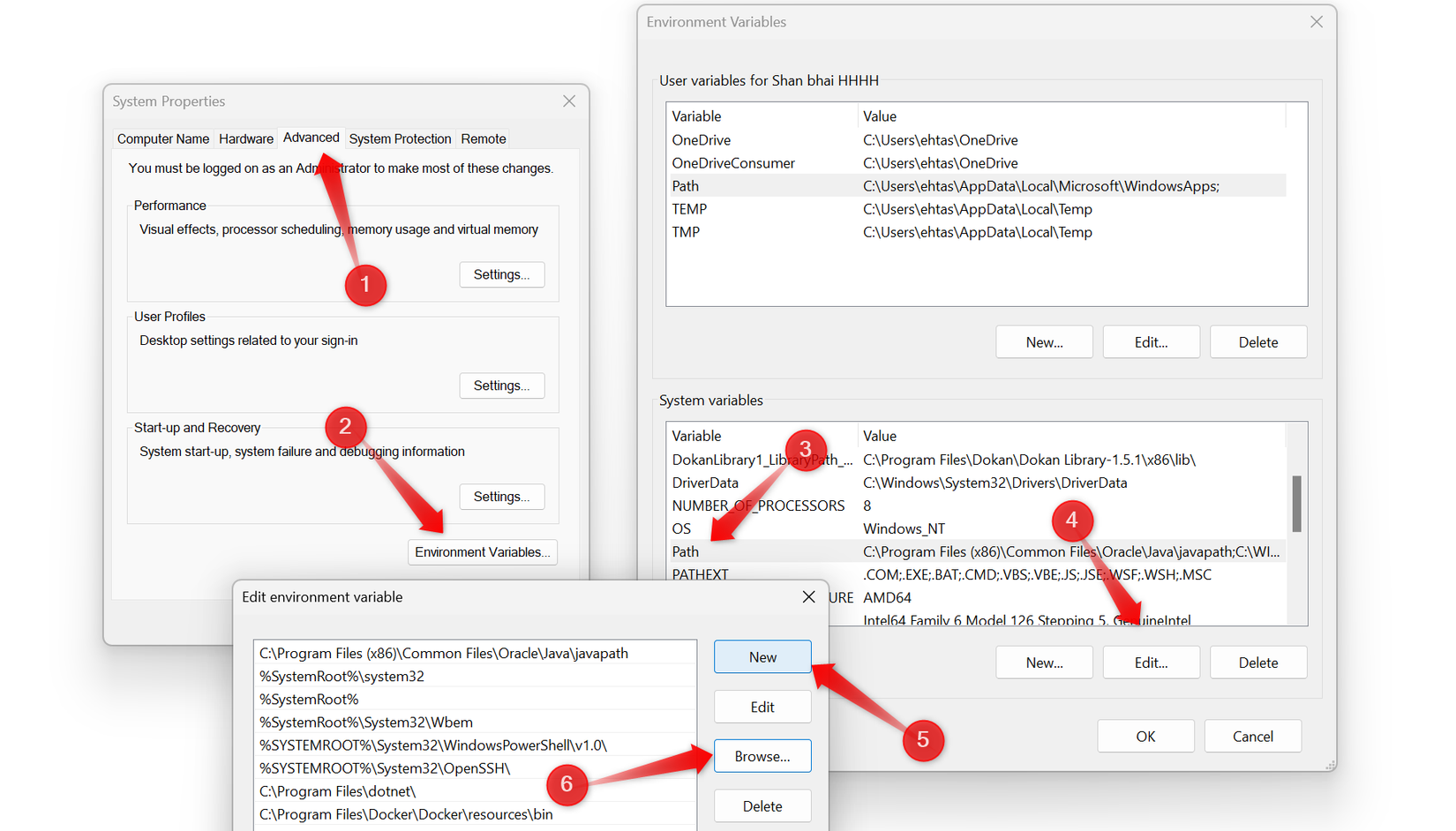
sDelete isn’t included with Windows by default, so you’ll need to download it manually. Head to Microsoft’s Sysinternals website, download the sDelete ZIP file, save it to your PC, and extract it to C:\Program Files. Next, type View advanced system settings, open the matching result, switch to the “Advanced” tab, and click “Environment Variables”.
Under System Variables, select the “Path” entry and click “Edit”. Choose “New” to add a fresh line, then click “Browse” to select a folder. Navigate to C:\Program Files, select the extracted sDelete folder, and confirm with “OK.” This updates your system’s PATH and completes the basic setup for sDelete.
How to use sDelete to erase files permanently
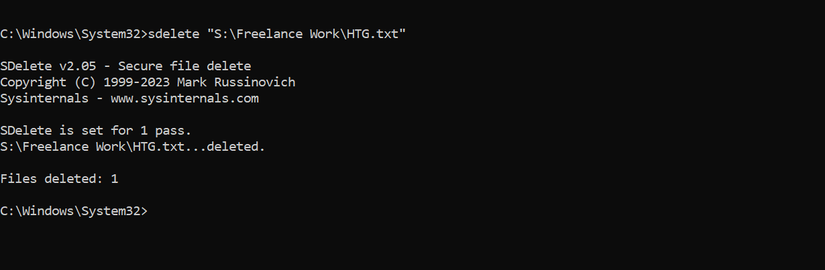
To securely delete a file with sDelete, first copy its full file path. Navigate to the folder containing the file, right-click it, and select “Copy as Path.” Then, open Command Prompt, type sDelete followed by the full path (including the file extension), and press Enter. For example, to delete a file named HTG.txt, type sDelete, paste the path, and hit Enter—the file will be securely deleted.
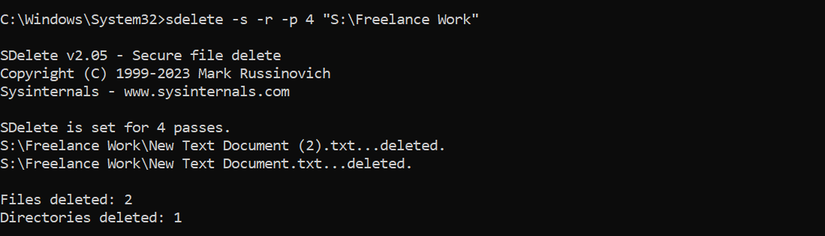
To delete an entire folder along with its subdirectories and any read-only files, use the -s and -r parameters before the folder path:
sDelete -s -r
This command will display the number of directories and files that were deleted.
sDelete -s -r -p 4
Other ways to securely wipe SSDs besides sDelete
You can rely on sDelete to securely wipe sensitive files on a drive you’ll continue using—especially if it’s a Hard Disk Drive (HDD). For Solid State Drives (SSDs), though, the safest method is to enable full-drive encryption with BitLocker and then securely remove the encryption keys, which makes all previously stored data inaccessible.
If you’re planning to sell or hand your PC over, it’s better to use Windows’ built-in reset tool. Right-click the Start button, open “Settings,” then navigate to System > Recovery. Click “Reset PC,” choose “Remove Everything,” and follow the prompts to securely wipe all your data.
If you once believed that deleting a file completely removes it from your drive, you now know that’s not the case. sDelete is a powerful solution, but it doesn’t need to be used for every deletion—reserve it for sensitive files. Also, keep in mind that files deleted with sDelete cannot be recovered, even with advanced recovery tools. So you could end up losing data if you delete a file by mistake.



Leave A Comment?