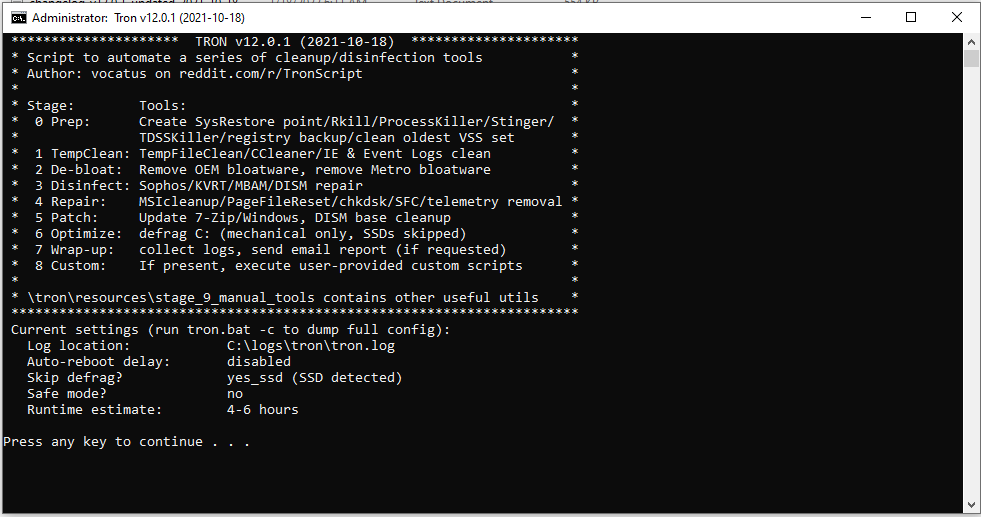
TronScript as the name implies is a script that will get badly-running Windows system back on its feet. You can download it here, but before that, you may need to disable the windows firewall or other anty viruses that you have. Why? Because the downloaded folder contains tools that temper with telemetry data.
Windows telemetry data includes basic system diagnostics information, logs of how frequently you use features and applications, system files, and likely more metrics that have yet to be disclosed. Fortunately, Microsoft allows users to set the amount of data they wish to share, on certain windows operating systems can’t be turned off.
You want to open the downloaded folder and run the tron with admin rights. 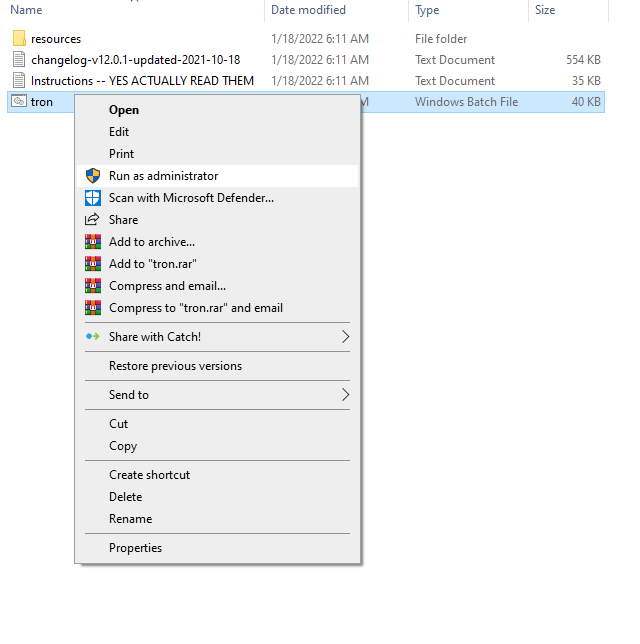
Click on More info then on Run anyway.
Now you need to type “I AGREE” all caps.
This process can take several hours depending on the computer.
So what does it do?
- First, it will create a restore point in case the changes are not to your liking.
- Removes temporary, event logs and the windows update kits. This can take a lot of space on your computer.
- Removes bloatware, for example, 3d viewer, 3d printing which most people don’t use.
- It will run several tools for removing viruses, rootkits, malware, spyware, adware, etc.
- It will clean the windows image of present bugs.
- It will repair the window image of any tearing that happened in the cleaning process.
- Defragmenting of hard drive, making for faster access to the file (defragmenting is skipped on SSD, not needed).
- In the end, it will leave logs with what it has done in the same file as the script.
Pretty nice I would say, but be aware that windows update may revert back some of the changes, such as the removed bloatware, TronScript is mostly recommended to computers that have a hard time with regular tasks.
[mai mult...]