Situatie
High CPU usage can slow down a system, cause overheating, or lead to crashes. Diagnosing the issue involves checking active processes, analyzing system logs, and identifying resource-hungry applications.
Solutie
Step 1: Identify High CPU Processes with top
The top command provides a real-time overview of running processes.
Run: top -o %CPU
You’ll see a list of running processes sorted by CPU consumption, with details like process ID (PID), user, memory usage, and execution time. Press 1 to view per-core CPU usage. Press q to exit.
Step 2: Get a Detailed View with ps
To list all processes consuming CPU along with their command lines, use:
ps aux –sort=-%cpu | head -10
This output displays:
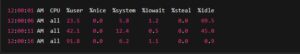
Step 3: Check CPU Usage History with sar
To analyze CPU usage trends over time, install sysstat:
sudo apt install sysstat
Then run: sar -u 5 10
This captures CPU usage every 5 seconds for 10 intervals:
A sudden increase in %system or %iowait might indicate a background process or disk-related issue.
Step 4: Find and Stop Rogue Processes
Once you’ve identified a problematic process, kill it with:
sudo kill -9 PID
Example: sudo kill -9 12345
If the process restarts, check if it’s running as a system service:
systemctl status <service-name>
Disable it if necessary:
Step 5: Prevent High CPU Usage in the Future
If a specific app is consuming excessive CPU, limit its resources using cpulimit:
This restricts Firefox to 50% CPU usage.


Leave A Comment?