Situatie
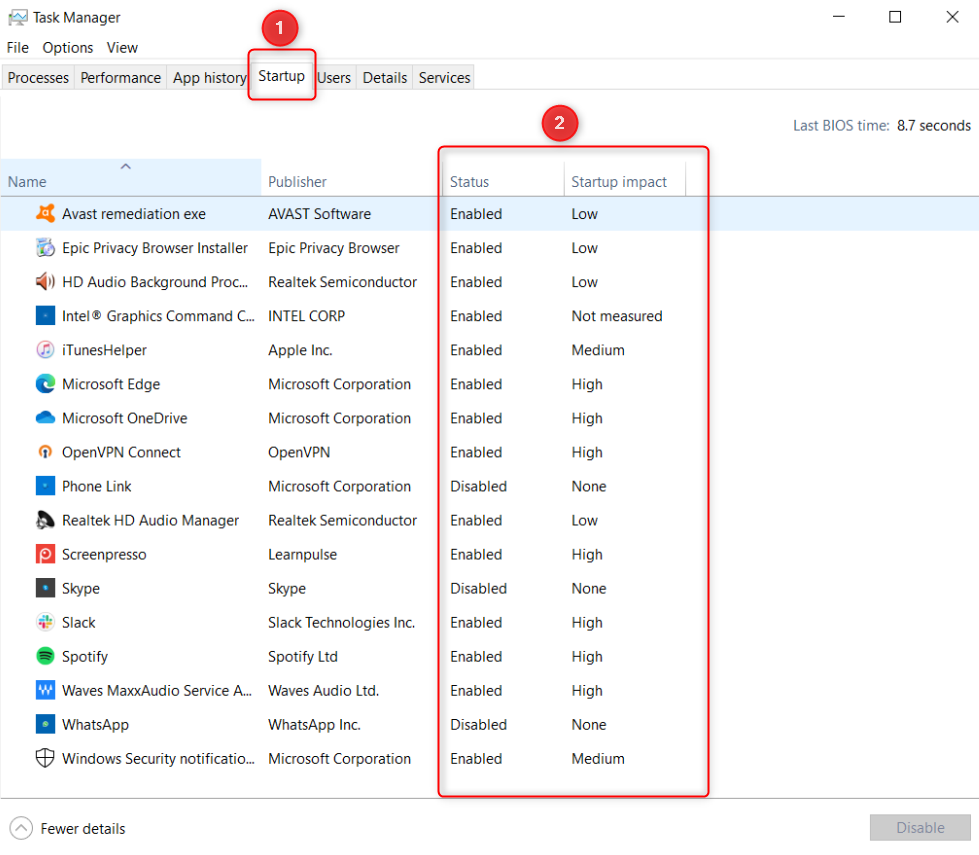
Disable Startup Programs in Task Manager
The Windows Task Manager is a handy tool that, in addition to showing currently active programs, also reveals applications that are part of your computer’s startup process.
To access Task Manager, press Ctrl+Alt+Del and select “Task Manager.” On Windows 10, switch to the “Startup” tab at the top. On Windows 11, select “Startup apps” from the left sidebar.
Each row lists an application alongside details relating to the startup. The “Status” column shows if the application is enabled or disabled on startup, and “Start-up Impact” scores based on the program’s impact on the CPU or disk (High, Medium, Low, or Not measured). This data helps you determine if you want an app to automatically launch when you log in to your computer.
If you want more information, right-click an existing column and select, in turn, which columns to add.
Solutie
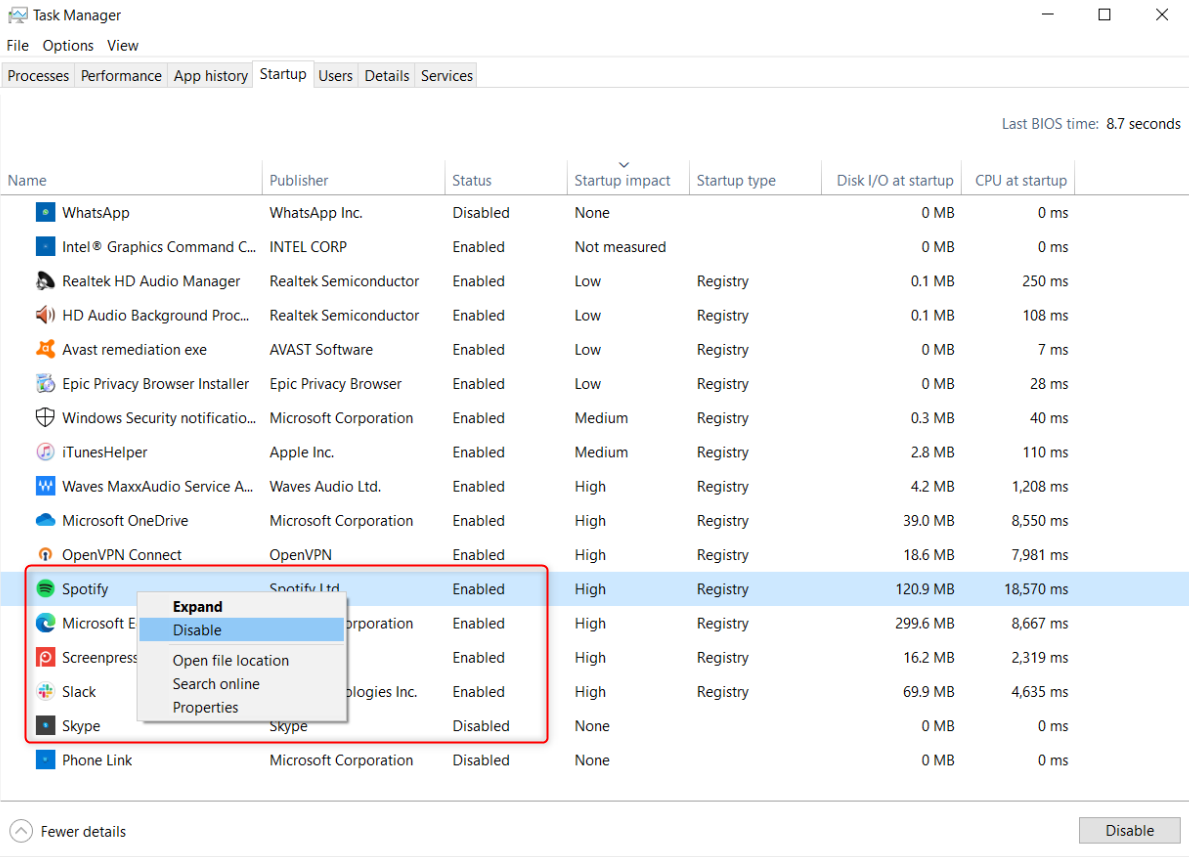
- Start-up type: Shows the source of the application, like from the registry or a folder. This is sometimes blank, which indicates the program is probably from the Microsoft Store.
- Disk I/O at start-up: Shows how much data is read and written from the disk when booting, which helps determine if your hard drive is overworked during the boot process.
- CPU at start-up: Shows how much time it takes the CPU to process its startup, measured in milliseconds.
You can use this information to identify programs that you don’t need to automatically launch, with a focus on those that are particularly resource-heavy. For example, gaming clients like Steam and messaging applications like Slack often run at startup so that they can run updates in the background and be quickly accessible. But if you rarely use these programs, you don’t need them slowing your startup.
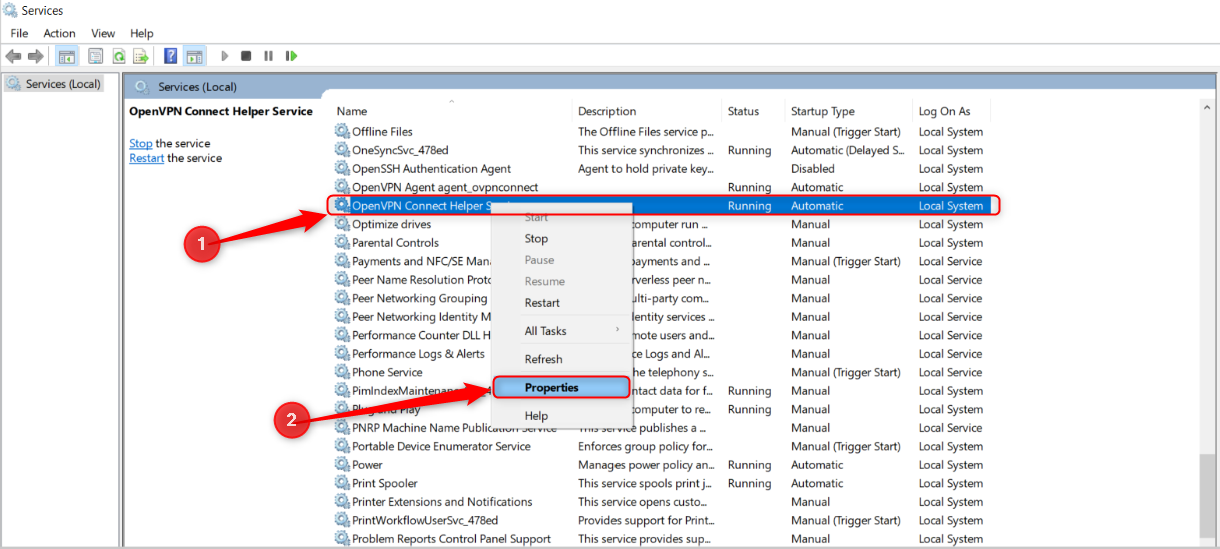
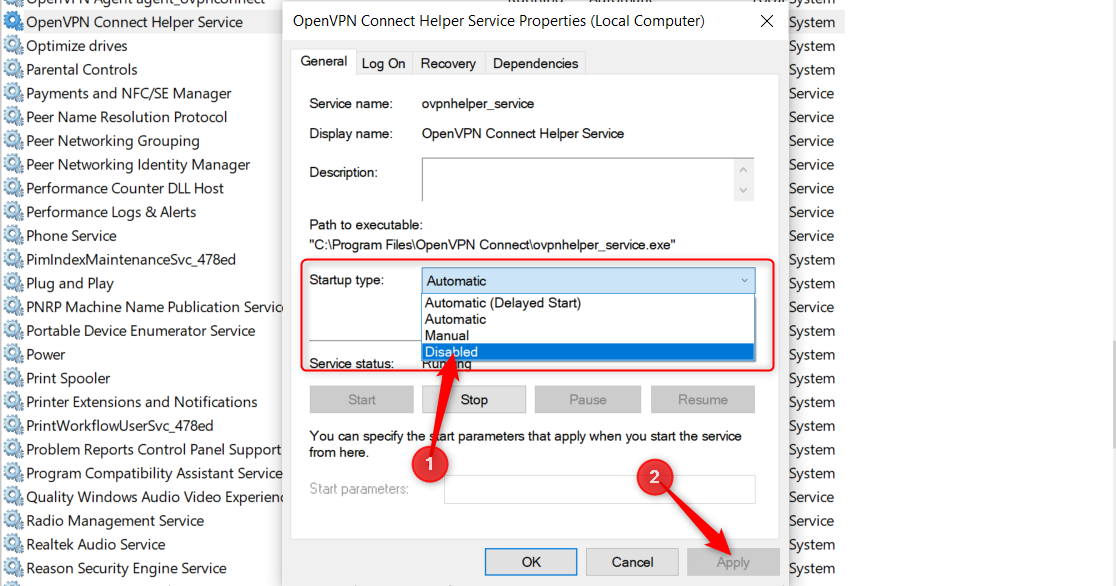
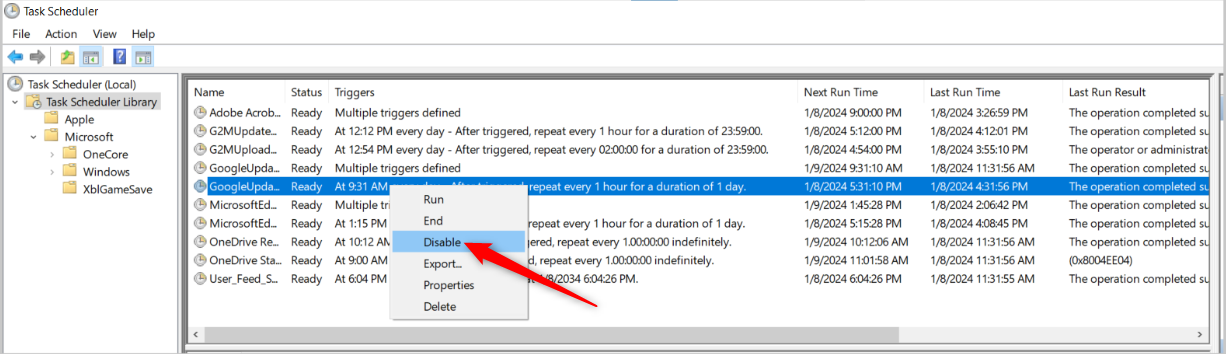
To remove a program from startup, right-click it and select “Disable.”
Remove Programs, Scripts, and Shortcuts From the Startup Folders
Your computer has a special folder where you can add programs to the Windows startup. You may not need to access this folder regularly or add anything here as a standard user, but knowing how to get here is important because you may need to delete programs that have added themselves to your boot process.
So, if you find any unfamiliar program in the Task Manager, you can head over to the startup folder and delete it instead of just disabling it. The folder may also contain scripts and shortcuts that may not appear in Task Manager.
- If you have multiple users on your computer, each individual will have different startup folders. There’s also a general startup folder for the whole PC. Changes in the user startup folder will only affect the currently logged-in user, while changes in the general startup folder will impact all users.To access the startup folder, first press Win+R to open Run. Enter shell:startup for current user programs or shell:common startup for system-wide startup programs, then click “OK.”
Your startup folder might be empty, depending on how new your computer is or what applications you’ve downloaded. If that’s the case, you have no action to take.When you’ve identified something you want to remove from your startup process, right-click it and select “Delete.”
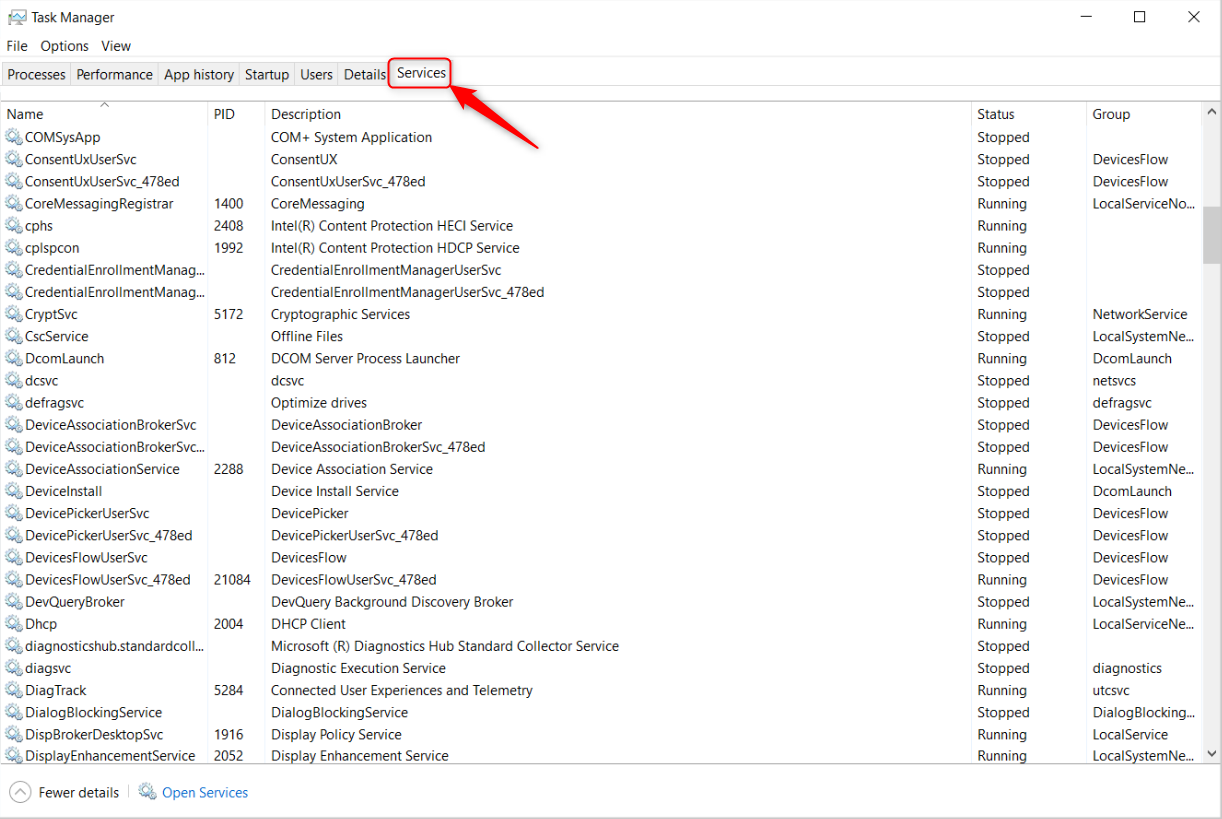
Disable Unnecessary Windows Services
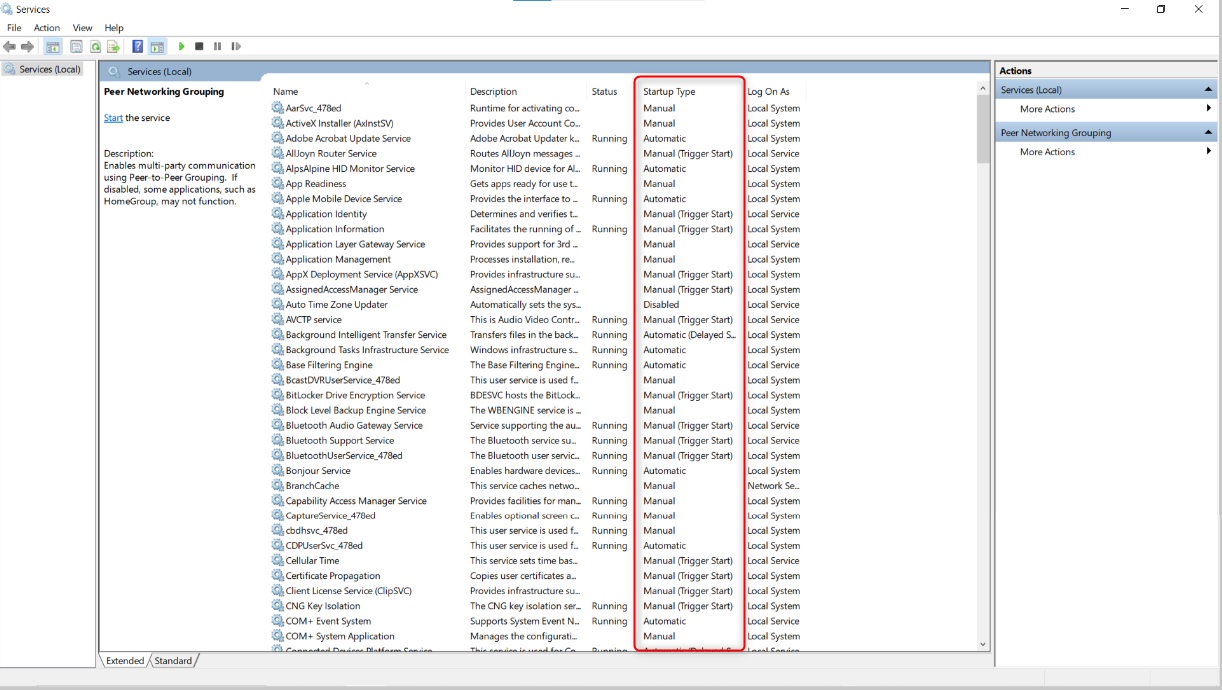
Windows Services is a great place to check for programs that might be draining resources. There are Windows services required to run the PC and third-party services that are installed when you install an application.
Windows services are programs responsible for background processes—you’re unlikely to see them open in your taskbar, for example. However, you can see them in Task Manager. Press Ctrl+Alt+Del, open Task Manager, and switch to the “Services” tab (at the top on Windows 10, or the left on Windows 11).

Leave A Comment?