Situatie
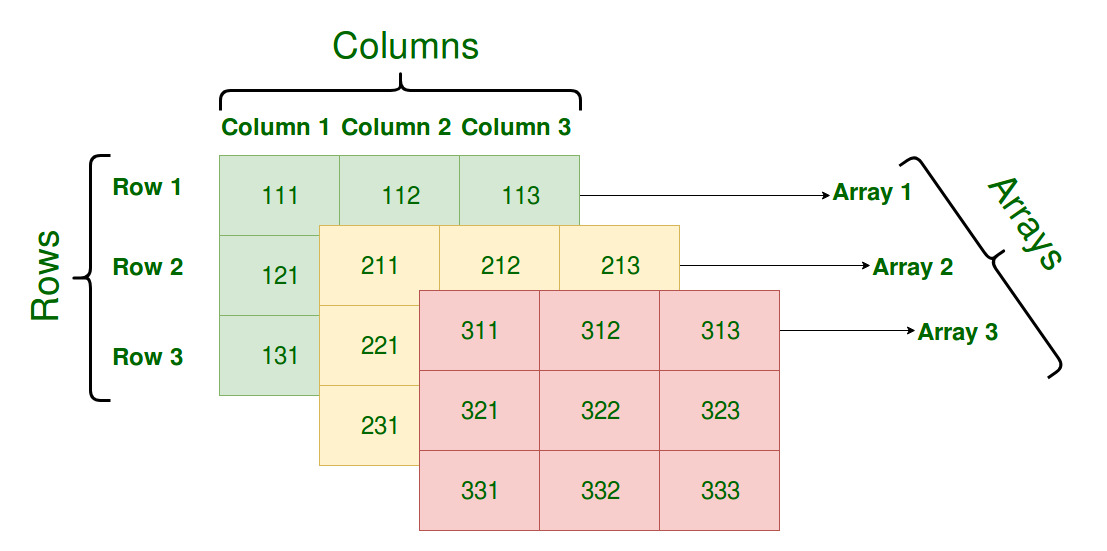
Initializing Three-Dimensional Array: Initialization in a Three-Dimensional array is the same as that of Two-dimensional arrays. The difference is as the number of dimensions increases so the number of nested braces will also increase.
Solutie
Pasi de urmat
Method 1:
int x[2][3][4] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19,
20, 21, 22, 23};
Better Method:
int x[2][3][4] =
{
{ {0,1,2,3}, {4,5,6,7}, {8,9,10,11} },
{ {12,13,14,15}, {16,17,18,19}, {20,21,22,23} }
};
Accessing elements in Three-Dimensional Arrays: Accessing elements in Three-Dimensional Arrays is also similar to that of Two-Dimensional Arrays. The difference is we have to use three loops instead of two loops for one additional dimension in Three-dimensional Arrays.
// C++ program to print elements of Three-Dimensional
// Array
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// initializing the 3-dimensional array
int x[2][3][2] =
{
{ {0,1}, {2,3}, {4,5} },
{ {6,7}, {8,9}, {10,11} }
};
// output each element’s value
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; ++j)
{
for (int k = 0; k < 2; ++k)
{
cout << “Element at x[” << i << “][” << j
<< “][” << k << “] = ” << x[i][j][k]
<< endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}

Leave A Comment?