How to use Run as to start an application as an administrator in Windows
You can use Run as to start an application as an administrator if you want to perform administrative tasks when you are logged on as a member of another group, such as the Users or Power Users group.
Steps to start an application as an administrator
To use Run as to start an application as an administrator, follow these steps:
- Locate the application that you want to start in Windows Explorer, the Microsoft Management Console (MMC), or Control Panel.
- Press and hold down the SHIFT key while you right-click the executable file or the icon for the application, and then select Run as.
- Select The following user.
- In the User name and Password boxes, type the administrator account and password, and then select OK.
In Windows 8 and Windows 10 start menu, it is possible to run a program or command with elevated privileges by simply right-clicking on the entry in the start menu or in the start menu search results and choosing Run as Administrator:
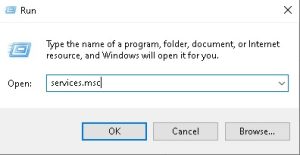
To launch a program with elevated rights via the Windows run dialog, follow the steps below:
1. Use windows key + R to launch the run dialog or Type run in windows search and select it.
2. Type in the name of the process you wish to launch with admin rights (for example, services.msc or cmd.exe, and then press (at the same time) ctrl + shift + Enter.