Cum rezolvăm alerta “SMTP Address Has No Mailbox Associated”
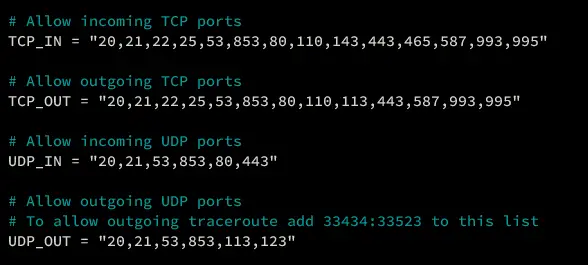
Când utilizați instrumente de acces programatic pe căsuță, cum ar fi Exchange Web Services (EWS) sau Microsoft Graph API pe Exchange Server 2016/2019/SE local sau Exchange Online, poate apărea eroarea „The SMTP address has no mailbox associated”. Acest lucru înseamnă, de obicei, că adresa SMTP specificată nu poate fi asociată unei căsuțe active.
Această problemă poate apărea atunci când utilizați instrumente terțe pentru a vă conecta la o căsuță Exchange prin EWS, cum ar fi instrumente de migrare sau de backup(cum ar fi Veeam), scripturi Python sau PowerShell sau alte aplicații bazate pe EWS.
Conform mesajului de eroare, adresa de e-mail SMTP specificată nu poate fi rezolvată într-o căsuță. Asigurați-vă că scriptul conține o adresă de e-mail sursă sau țintă existentă și că aceasta corespunde adresei SMTP principale a utilizatorului.
[mai mult...]