Situatie
Solutie
To install TLP, simply open a terminal (press Ctrl+Alt+T) and enter the following command:
sudo apt install tlp tlp-rdwOnce installed, TLP will start automatically whenever your computer boots. It works right out of the box with default settings that are optimized for most users. You can enter the following command to view the settings and status of various system components.
sudo tlp-stat
For more precise data, tlp-stat has several flags you can use like -c for the active configuration or -t for the temperature and fan speed.
If you’re comfortable making advanced tweaks, you can edit TLP’s configuration file at /etc/tlp.conf to fine-tune power settings. However, for most users, the default settings will provide noticeable improvements without any extra effort. You should make a backup copy of the original file before you change anything.
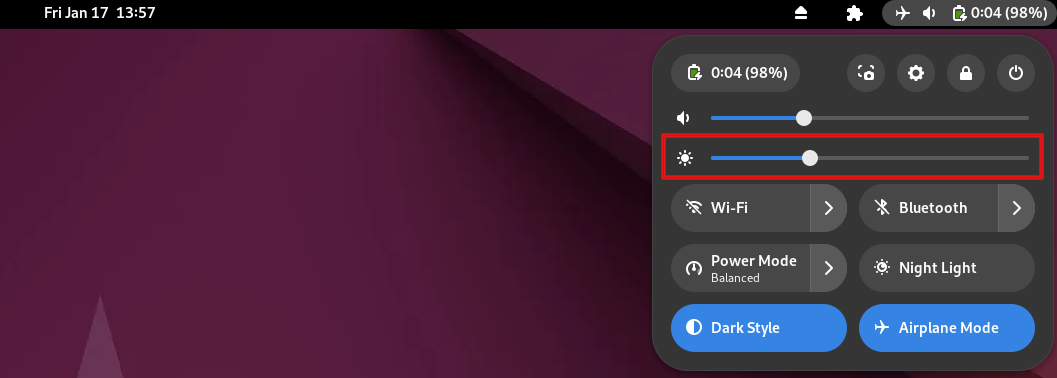
Your screen is one of the biggest sources of power drain on your laptop. Reducing the brightness can significantly improve battery life. Many laptops have special keys to raise and lower the brightness. If yours doesn’t, you can set the brightness from the system menu at the top-right corner of the desktop (the menu you open to shut down or restart your computer).
Enable Automatic Brightness (If Supported)
If your laptop has a light sensor, Ubuntu may have an option to adjust brightness automatically. Enabling this feature ensures that brightness is optimized based on your surroundings. If your lap supports this function, you’ll find it under the “Power” section of the system settings.
Unnecessary hardware components, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and external USB devices, can drain your battery even when you’re not using them.
Disable Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
If you’re not using the internet or Bluetooth peripherals, turn these off to save power. You can do this via the system settings or by running these commands in the terminal:
To turn off Wi-Fi:
nmcli radio wifi off
To turn off Bluetooth:
rfkill block bluetooth
Disconnect External Devices
USB devices like external hard drives, USB flash drives, and even mice and keyboards consume power. Unplug them when you’re not using them to maximize battery life.
Optimize CPU Performance
Enter the following command in your terminal to install cpufrequtils:
sudo apt install cpufrequtilsSet the CPU to power-saving mode:
sudo cpufreq-set -g powersave
This lowers the CPU’s speed when high performance isn’t needed, reducing power consumption.
Manage Background Applications
Unnecessary background processes use up CPU power and drain your battery faster. Many programs stay running in the background when you close them—especially messaging apps like Slack and Telegram. Shutting down background apps that you aren’t using can significantly increase your battery life.
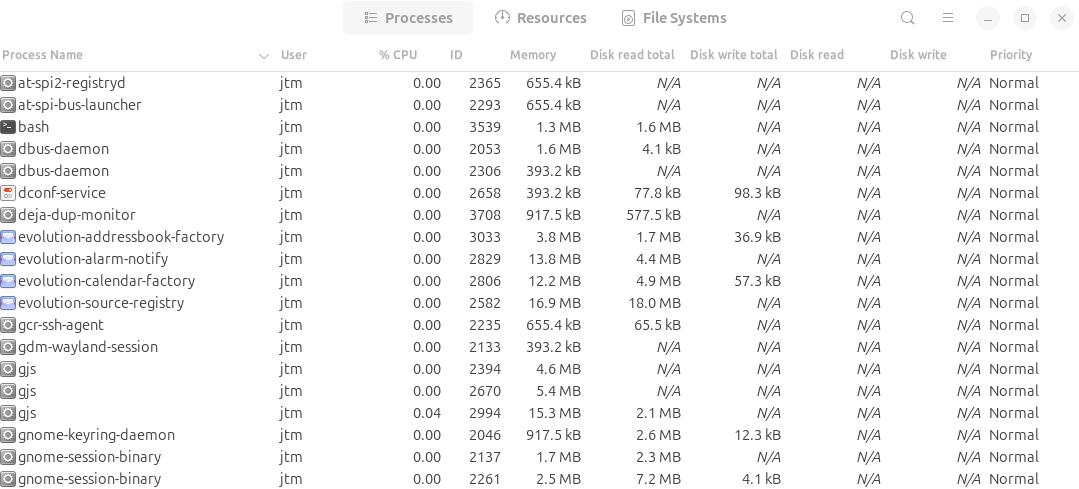
Check Running Processes
The Linux top utility is great when you just want to check quickly for any obviously misbehaving programs on your system. If you notice any tasks with high memory or CPU usage, you may benefit by shutting them down (see below) if they aren’t related to a necessary system process or an app that you are using. Simply press “Q” to quit and return to the terminal prompt.
How to Close Unnecessary Applications
If you notice a program consuming a lot of power, you can close it using the following command:
killall application_name
If you get an error saying you don’t have permission to close a task, prefix the command above with “sudo”.
Be careful when ending processes, especially when using sudo—you don’t want to accidentally close essential system tasks!
There are a few steps you can take to generally optimize your system for less battery drain.
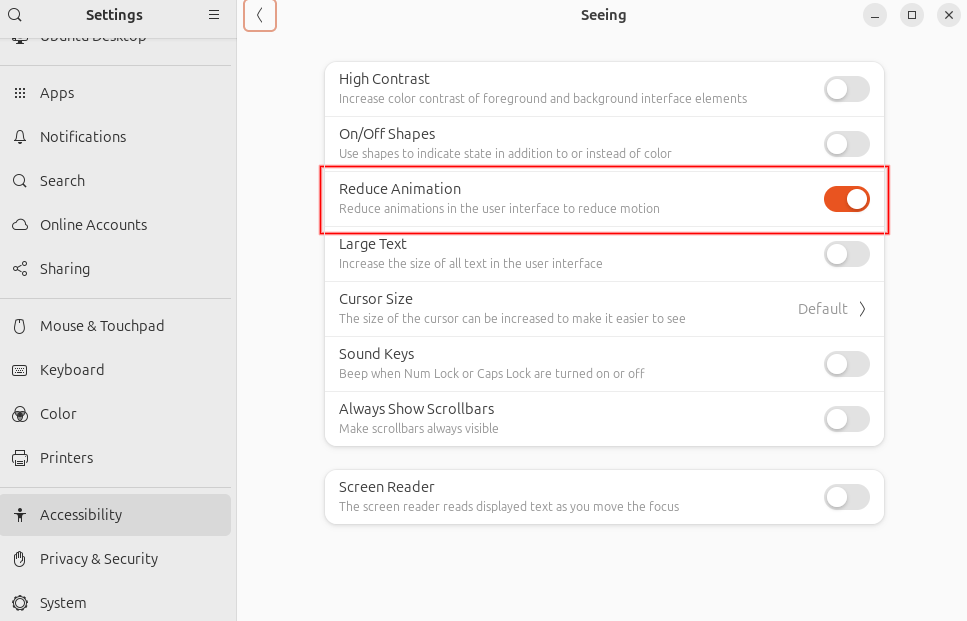
Reduce Visual Effects
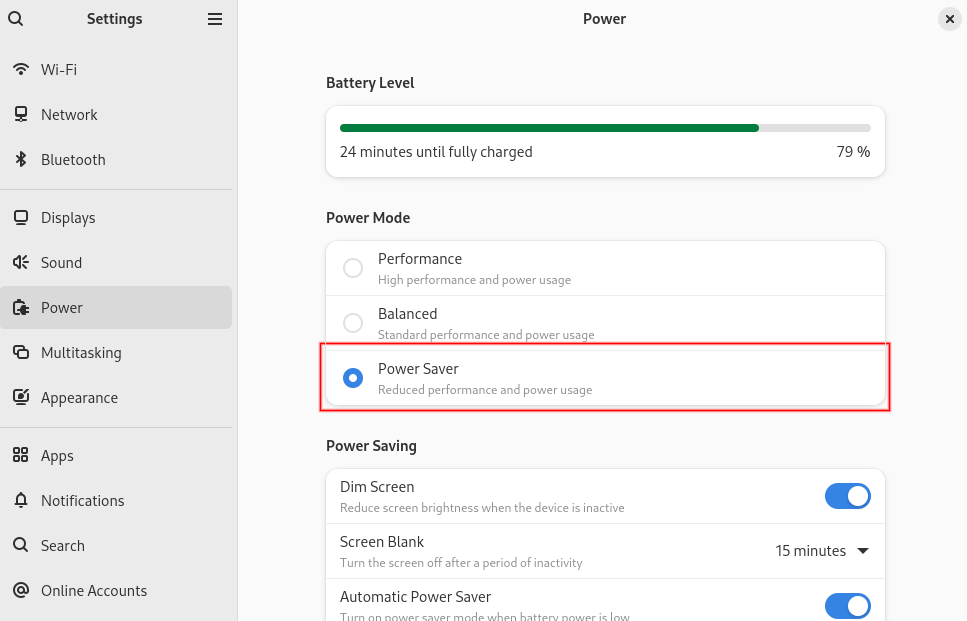
Enable Power Saver Mode
Ubuntu includes a built-in Power Saver profile that automatically adjusts settings for better battery life. To enable it, open Settings. Then navigate to “Power” and select the “Power Saver” mode.

Leave A Comment?