- System Stability: Ensuring you have enough power prevents system crashes and instability, especially during high-performance tasks like gaming or video editing.
- Component Protection: A power supply that provides insufficient wattage can damage your PC components over time.
- Future Upgrades: Knowing your current PSU’s wattage helps plan for future upgrades without needing to replace the power supply prematurely.
1. Check the PSU Label
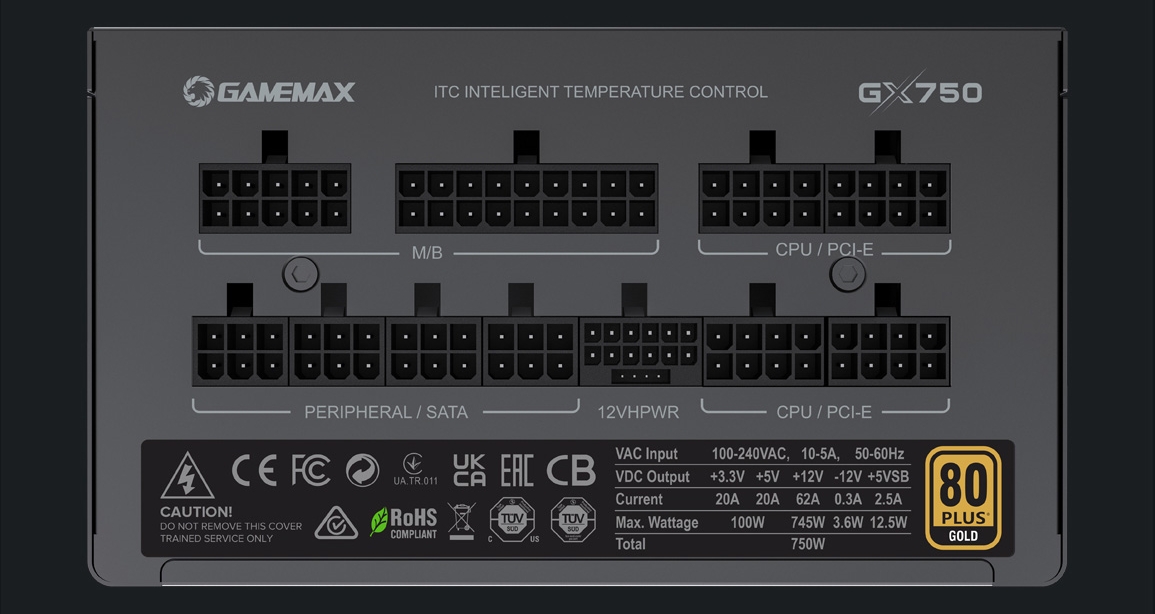
The simplest way to find out your PSU’s wattage is by checking the label on the power supply itself.
- Turn Off and Unplug Your PC: For safety, ensure your computer is powered off and disconnected from any electrical outlets.
- Open the PC Case: Remove the side panel of your computer case to access the power supply.
- Locate the PSU: Find the power supply unit, usually located at the top or bottom of the case.
- Read the Label: Look for a label on the side of the PSU. It should provide various details, including the wattage. The wattage is often listed as “Max Power” or “Total Power” and might be followed by a wattage value (e.g., 500W).
2. Check your PC’s Documentation
If you have the documentation for your PC or its components, it might include details about the power supply.
- Consult the Manual: Look through the PC’s manual or any build guides you used when assembling the system. The PSU wattage might be listed there.
- Check Manufacturer Specifications: If you bought a pre-built PC, you could often find the PSU specifications on the manufacturer’s website or in the product specifications.
3. Use Software Tools
There are some software tools available that can provide information about your system’s power consumption, but they might not directly show the PSU wattage.
- Download a Monitoring Tool: Programs like HWMonitor or CPU-Z can show detailed information about your system’s components and their power consumption.
- Estimate Power Draw: While these tools won’t directly tell you the PSU wattage, they can help you estimate your system’s power draw, which can guide you in choosing an appropriate PSU if you’re upgrading.
4. Consult a Professional
If you’re unsure or uncomfortable opening your PC Case, consider consulting a professional technician.
- Visit a Computer Repair Shop: Technicians can quickly identify your PSU’s wattage and provide advice on whether it meets your system’s needs.