Depanare
Artefacte grafice (ale texturilor) in aplicatii 2D sau 3D pe terminale iOS/Android (ARM)
Daca se respecta anumite “conditii”, desi dispozitivul este sau a fost perfect functional fara a avea disfunctionalitati de natura hardware, putem observa ca in anumite aplicatii si/sau motoare grafice texturile/imaginile/loading bars fie sunt albe sau incarca lent, fie prezinta tipare de culori la intamplare.
Desigur, sunt posibile si alte simptome dar cele de mai sus au fost observate si remediate cu metoda prezentata in continuare.
[mai mult...]Imposibilitate finalizare instalare sistem de operare (x64) prin retea (RJ-45)
Daca anumite dispozitive nu pot finaliza instalarea sistemului de operare conectate la un cablu ethernet folosind network boot desi utilizarea “aceluiasi post de lucru” nu prezinta probleme pe alte device-uri (inclusiv noi), mai exista o ultima solutie inaintea necesitatii inlocuirii de componente sau trimiterea in garantie.
[mai mult...]Tutorial pentru comanda chmod în Linux pentru începători
Comanda chmod din Linux este utilizată pentru a modifica permisiunile fișierelor și directoarelor într-un sistem de operare bazat pe Linux. Aceasta permite utilizatorilor să definească cine poate citi, scrie sau executa un fișier prin modificarea setărilor de permisiuni. Permisiunile sunt de obicei atribuite la trei categorii: proprietarul fișierului, grupul căruia îi aparține fișierul și alții (toți ceilalți).
Comanda chmod poate fi utilizată cu notație simbolică (de exemplu, chmod u+x nume_fișier pentru a adăuga permisiunea de execuție pentru utilizator) sau cu notație numerică (de exemplu, chmod 755 nume_fișier pentru a seta permisiuni specifice de citire, scriere și execuție pentru fiecare categorie). Această comandă este esențială pentru gestionarea controlului accesului pe un sistem, asigurându-se că fișierele și directoarele au setările de securitate corespunzătoare.
Vă rugăm să rețineți că toate exemplele și instrucțiunile menționate în acest tutorial au fost testate pe Ubuntu 24.04, iar versiunea chmod pe care am folosit-o este 8.25.
Noțiuni de bază despre Chmod
Luați în considerare următorul exemplu de comandă ls :
Prima coloană din rezultat este de interes pentru noi. Lăsați deoparte semnul „-” inițial (care indică tipul de fișier). Câmpurile rămase din coloană pot fi defalcate în continuare astfel: rw- , rw- și r–. Acestea sunt permisiunile pe care le au proprietarul fișierului, grupul căruia îi aparține fișierul și alte persoane asupra acestui fișier.
Aceasta înseamnă că proprietarul are atât permisiuni de citire (r), cât și permisiuni de scriere (w), la fel ca și grupul. Alții, însă, au doar permisiuni de citire pentru fișier. Rețineți că presupunem că utilizatorul curent deține fișierul.
Acum, să presupunem că cerința este de a acorda tuturor dreptul de a executa acest fișier. Iată cum se poate face acest lucru:
chmod +x script.sh
Iată permisiunile acum:
„X”-ul suplimentar din permisiunile pentru proprietar, grup și alte persoane semnifică faptul că toată lumea are acum acces de execuție pentru acest fișier.
Totuși, cel mai probabil este să nu doriți ca toată lumea să aibă acces de execuție pentru un fișier. Ce se întâmplă dacă cerința este de a acorda acces de execuție la script.sh doar proprietarului/utilizatorului curent. Ei bine, pentru aceasta, primul pas acum ar fi să retrageți accesul de execuție de la toată lumea, lucru pe care îl puteți face folosind următoarea comandă:
chmod -x script.sh
Și apoi acordă-l explicit proprietarului:
chmod u+x script.sh
După cum ați fi ghicit, „u+x” spune să acorde (+) proprietarului/utilizatorului curent (u) acces de execuție (x) la fișier. În mod similar, pentru grup, puteți folosi „g”, iar pentru alții puteți folosi „o”.
Rețineți că ori de câte ori doriți să acordați/revocați un set comun de permisiuni către/de la toți, puteți folosi „a” în loc de „ugo”. Ceea ce vreau să spun este:
chmod ugo-x script.sh
poate fi înlocuit cu acesta:
chmod ax script.sh
De asemenea, rețineți că, dacă niciuna dintre acestea („u”, „g”, „o” și „a”) nu este specificată explicit, atunci se presupune că și valoarea implicită este „a”. Continuând, dacă doriți, puteți, de asemenea, să copiați pur și simplu permisiunile acordate, de exemplu, proprietarului/utilizatorului curent și să le păstrați pentru grup sau pentru alții. Pentru aceasta, utilizați semnul „=”.
De exemplu, pentru a copia permisiunile de proprietar/utilizator într-un grup, utilizați următoarea comandă:
chmod g=u script.sh
Un alt scenariu ar putea fi copierea permisiunilor pentru un anumit fișier și păstrarea acestora pentru fișierul dvs. Pentru aceasta, utilizați opțiunea de linie de comandă –reference . Iată șablonul general pentru utilizarea acestei opțiuni de linie de comandă:
chmod --reference=[fișier-sursă] [fișier destinație]
În comanda de mai sus, fișier-sursă este fișierul ai cărui biți de permisiune doriți să îi copiați, iar fișier-destinație este fișierul ai cărui biți de permisiune doriți să îi modificați.
Mergând mai departe, există și o notație numerică (cunoscută și sub numele de reprezentare octală) folosind care poți spune lui chmod să modifice permisiunile. Există trei numere cu care te joci în acest mod: 4, 2 și 1. În timp ce 4 este pentru citire, celelalte două sunt pentru scriere și respectiv executare.
De exemplu, luați în considerare următorul exemplu:
Acum, să presupunem că sarcina este de a adăuga permisiunea de execuție pentru proprietar/utilizator, de a elimina permisiunea de scriere, dar de a adăuga permisiunea de execuție grupului și de a elimina toate permisiunile de la ceilalți. Acest lucru se poate face după cum urmează:
chmod 750 script.sh
În comanda de mai sus, „7” este pentru utilizator, rezultatul a 4+2+1, deoarece cerința pentru utilizator este să dețină toate permisiunile. În mod similar, „5” este pentru grup, rezultatul a 4+0+1, deoarece cerința este de a acorda grupului doar permisiuni de citire și execuție. În cele din urmă, „0” este pentru ceilalți, rezultatul a 0+0+0, deoarece cerința este de a revoca toate permisiunile celorlalți.
Pentru cei care lucrează cu linkuri simbolice, iată câteva lucruri de știut:
chmod nu modifică niciodată permisiunile legăturilor simbolice; apelul de sistem chmod nu poate modifica permisiunile acestora. Aceasta nu este o problemă, deoarece permisiunile legăturilor simbolice nu sunt niciodată utilizate. Cu toate acestea, pentru fiecare legătură simbolică listată în linia de comandă, chmod modifică permisiunile fișierului indicat. În schimb, chmod ignoră legăturile simbolice întâlnite în timpul traversărilor recursive de directoare.
Referință linie de comandă
Comanda chmod din Linux are mai multe opțiuni în linia de comandă care îi modifică comportamentul. Iată o listă cu cele mai frecvent utilizate opțiuni:
- -R, –recursive: Această opțiune aplică recursiv modificările permisiunilor tuturor fișierelor și directoarelor din directorul specificat. Este utilă atunci când doriți să modificați permisiunile unui director și ale întregului său conținut dintr-o dată.Exemplu: chmod -R 755 /calea/către/director
- -c, –changes: Această opțiune raportează doar când se face o modificare. Dacă permisiunile sunt modificate cu succes, afișează un mesaj care indică modificarea.Exemplu: chmod -c 644 numefișier
- -v, –verbose: Această opțiune oferă informații detaliate despre fiecare fișier procesat, indiferent dacă permisiunile au fost modificate sau nu.Exemplu: chmod -v 755 numefișier
- -reference=RFILE: În loc să specificați direct permisiunile, această opțiune vă permite să setați permisiunile unui fișier sau director pentru a se potrivi cu un alt fișier sau director (RFILE).Exemplu: chmod –reference=file1 file2
- -f, –silent, –quiet: Această opțiune suprimă majoritatea mesajelor de eroare, făcând comanda să se execute fără a afișa rezultatul pentru erori.Exemplu: chmod -f 755 numefișier
Aceste opțiuni permit utilizarea flexibilă a chmod în diverse scenarii, de la ajustări ale unui singur fișier până la modificări ale permisiunilor directorului la scară largă.
[mai mult...]Linux env Command Tutorial For Beginners
Comanda Linux env este utilizată pentru a afișa și gestiona variabilele de mediu într-o sesiune shell. Variabilele de mediu sunt valori dinamice care afectează procesele sau programele care rulează în shell, cum ar fi căile către fișierele executabile, setările specifice utilizatorului și comportamentul sistemului. Prin rularea comenzii env fără argumente, aceasta listează toate variabilele de mediu curente și valorile acestora. În plus, env poate fi utilizat pentru a executa o comandă cu un mediu modificat prin setarea temporară sau suprascrierea anumitor variabile de mediu pe durata comenzii respective. Acest lucru este util pentru testarea sau rularea programelor într-un mediu specific fără a modifica configurația globală.
Dar înainte de a face asta, merită menționat faptul că toate comenzile și instrucțiunile din acest tutorial au fost testate pe Debian 12 și Ubuntu 24.04.
Comandă Linux env
Prin definiție, comanda env vă permite să rulați un program într-un mediu modificat. Sintaxa comenzii, așa cum este menționată pe pagina sa de manual, este următoarea:
mediu [OPȚIUNE]... [-] [NUME=VALOARE]... [COMANDĂ [ARG]...]
Și iată ce spune pagina de manual despre mediu:
Setați fiecare NAME la VALUE în mediu și executați COMMAND.
Următoarele exemple în stil Întrebări și Răspunsuri ar trebui să vă ofere o idee mai bună despre cum funcționează această comandă:
Î1. Cum se accesează toate variabilele de mediu folosind comanda env?
Mediul Bash, după cum probabil știți deja, constă din intrări VARNAME=VALUE. Pentru a accesa toate variabilele de mediu, precum și valorile asociate acestora, executați comanda env fără nicio opțiune.
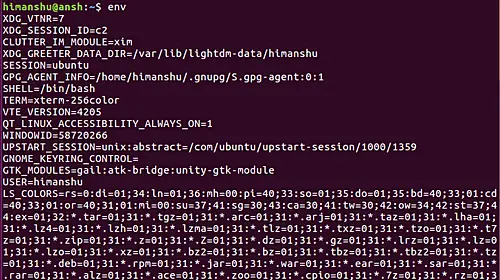
mediu
Iată rezultatul comenzii de mai sus în cazul nostru:
Î2. Cum se schimbă temporar mediul folosind env?
Caracteristica cheie a programului env este capacitatea de a modifica temporar mediul unui proces. De exemplu, am creat un mic fișier executabil — denumit env — care afișează valoarea variabilei de mediu USER la execuție.
Iată rezultatul în scenariul normal:
Acum, ceea ce am făcut a fost să folosim comanda env pentru a schimba temporar valoarea variabilei de mediu USER de la „himanshu” la „HTF” pentru executabil/proces. Iată comanda pe care am folosit-o în acest caz:
mediu UTILIZATOR=HTF ./mediu
Și iată rezultatul produs în acest caz:
Deci puteți vedea că executabilul a returnat noua valoare.
Notă: Așa cum sugerează sintaxa generică a instrumentului, puteți modifica valorile mai multor variabile de mediu și puteți face ca procesul să utilizeze aceste valori noi.
Î3. Cum se poate face ca un proces să ignore mediul existent folosind env?
Dacă doriți, puteți face ca un proces să ignore mediul existent/moștenit și să înceapă cu unul gol. Acest lucru se poate face folosind opțiunea -i sau –ignore-environment .
De exemplu:
Î4. Cum se face ca env să utilizeze NUL în loc de caracterul newline în ieșire?
În primul exemplu discutat mai sus, liniile de ieșire produse de env sunt separate prin linie nouă. Totuși, dacă doriți, puteți face ca env să utilizeze caracterul NUL ca separator. Această funcție poate fi accesată folosind opțiunea de linie de comandă –null .
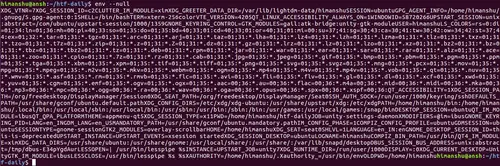
mediu --nul
Mai jos este un exemplu de captură de ecran;
Î5. Cum pot afla eroarea pe baza stării de ieșire a comenzii env?
Comanda env produce următoarele coduri de ieșire: 0, 125, 126 și 127. Următoarele sunt descrierile erorilor asociate:
0 dacă nu este specificată nicio COMANDĂ și mediul este afișat 125 dacă 'env' în sine eșuează 126 dacă COMMAND este găsită, dar nu poate fi invocată 127 dacă COMMAND nu poate fi găsită
Dacă primiți un cod de eroare diferit de cele menționate mai sus, aceasta este starea de ieșire returnată de procesul/comanda care a fost executată cu un mediu modificat.
[mai mult...]Transferul datelor de orice tip catre dispozitive cu iOS/iPadOS folosind wi-fi + VLC
Daca dorim sa transferam date catre un smartphone sau tableta Apple fara a utiliza iTunes ori a fi limitati la fotografii si inregistrari video, echipa VideoLan au pus la dispozitie aplicatia VLC inclusiv pe Apple AppStore cu functionalitatea de wi-fi sharing inclusa.
[mai mult...]