How to scan for open ports (security reasons) on Windows 11
Step 1: Open CMD or Command Prompt
- Press Win + R from your keyboard > Type cmd > Click on the Enter button
Step 2: Implement the “netstat” Command
An effective tool for keeping an eye on open ports within the system and configured network connections is the netstat command to simplify. It offers comprehensive details on all open connections and system servers, such as the protocol in use, and local and international addresses to control or verify all the connection’s status.
- Type the below command in the cmd to check the open port functions > Press Enter
netstat -an | find "LISTEN"
- See the output below
TCP 0.0.0.0:135 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING TCP 0.0.0.0:445 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING TCP 0.0.0.0:902 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
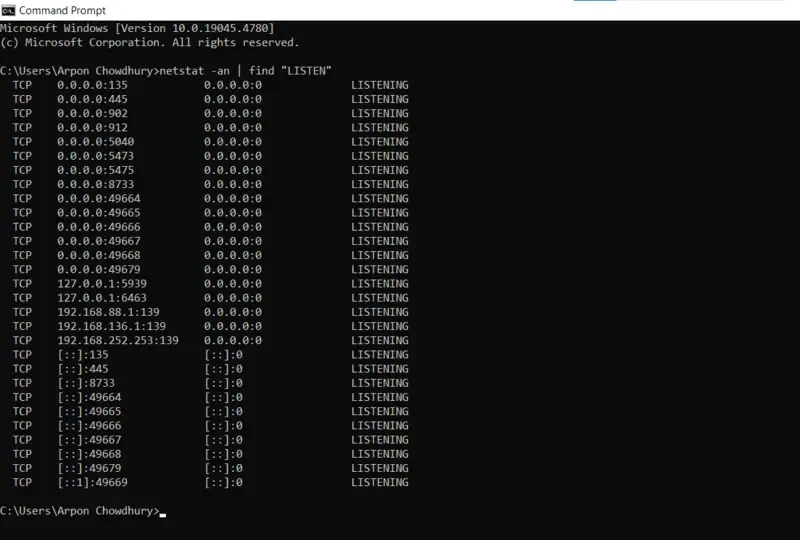
In this case, 0.0.0.0 designates that all pre-processed network interfaces are listening on the port, which is open for the internal system server. The port number is the number that comes after the colon of the system commands (e.g., 135, 445, 3389).
Step 3: Observe the functional Process using the Port
- Write the following command to identify which application or process is using a specific port within the system.
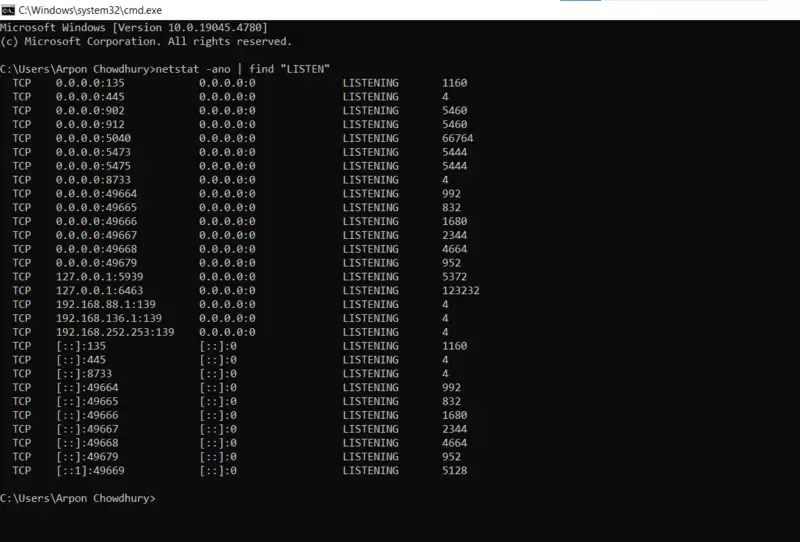
netstat -ano | find "LISTEN"
An extra -o flag is included with this command while processed, which shows the Process ID (PID) connected to each port manually.
- See the output within a PID column
TCP 0.0.0.0:135 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 1160 TCP 0.0.0.0:445 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 4
- Search and Open Task Manager > Go to Details option > See the PID column
Step 4: Check Specific Port in cmd
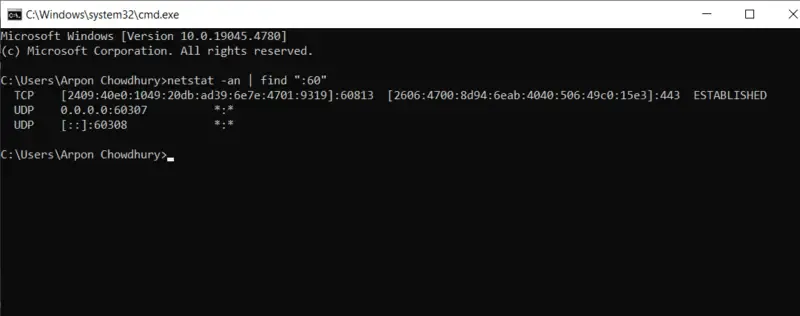
- You can change the implemented command to focus on a particular port if you want to see if it’s open or not within the system configuration. For instance, use this to see if port 60 is open to identify the process:
netstat -an | find ":60"
- See the final entry below –
TCP 0.0.0.0:40 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING